Tumor-Localized Secretion of Soluble PD1 Enhances Oncolytic Virotherapy
- PMID: 28314785
- PMCID: PMC5457316
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1638
Tumor-Localized Secretion of Soluble PD1 Enhances Oncolytic Virotherapy
Abstract
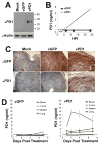
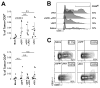
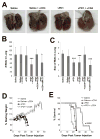
Oncolytic virotherapy represents an attractive option for the treatment of a variety of aggressive or refractory tumors. While this therapy is effective at rapidly debulking directly injected tumor masses, achieving complete eradication of established disease has proven difficult. One method to overcome this challenge is to use oncolytic viruses to induce secondary antitumor immune responses. Unfortunately, while the initial induction of these immune responses is typically robust, their subsequent efficacy is often inhibited through a variety of immunoregulatory mechanisms, including the PD1/PDL1 T-cell checkpoint pathway. To overcome this inhibition, we generated a novel recombinant myxoma virus (vPD1), which inhibits the PD1/PDL1 pathway specifically within the tumor microenvironment by secreting a soluble form of PD1 from infected cells. This virus both induced and maintained antitumor CD8+ T-cell responses within directly treated tumors and proved safer and more effective than combination therapy using unmodified myxoma and systemic αPD1 antibodies. Localized vPD1 treatment combined with systemic elimination of regulatory T cells had potent synergistic effects against metastatic disease that was already established in secondary solid organs. These results demonstrate that tumor-localized inhibition of the PD1/PDL1 pathway can significantly improve outcomes during oncolytic virotherapy. Furthermore, they establish a feasible path to translate these findings against clinically relevant disease. Cancer Res; 77(11); 2952-63. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


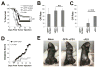

Similar articles
-
Engineering Newcastle Disease Virus as an Oncolytic Vector for Intratumoral Delivery of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Immunocytokines.J Virol. 2020 Jan 17;94(3):e01677-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01677-19. Print 2020 Jan 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31694938 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus 1 VC2 Promotes Long-Lasting, Systemic Anti-melanoma Tumor Immune Responses and Increased Survival in an Immunocompetent B16F10-Derived Mouse Melanoma Model.J Virol. 2021 Jan 13;95(3):e01359-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01359-20. Print 2021 Jan 13. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33177208 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Effective Combinations of Immune Checkpoint Blockade and Oncolytic Virotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;21(24):5543-51. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2009. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26187615 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of PD‑1/PD‑L1 inhibitors: The prospect of overcoming the weakness of tumor immunotherapy (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):362. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12001. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving antitumor efficacy via combinatorial regimens of oncolytic virotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2020 Nov 10;19(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01275-6. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33172438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trial Watch: Oncolytic viro-immunotherapy of hematologic and solid tumors.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Aug 27;7(12):e1503032. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1503032. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 30524901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Combination of Oncolytic Virotherapy and CAR T/NK Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Cancer].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2020 Jan-Feb;54(1):3-16. doi: 10.1134/S0026893320010100. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2020. PMID: 32163385 Review. Russian.
-
Immunomodulatory Arming Factors-The Current Paradigm for Oncolytic Vectors Relies on Immune Stimulating Molecules.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 22;22(16):9051. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169051. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Virus-Inspired Inhalable Liponanogel Induces Potent Antitumor Immunity and Regression in Metastatic Lung Tumors.Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 15;84(14):2352-2363. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-3414. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38718316 Free PMC article.
-
OV Modulators of the Paediatric Brain TIME: Current Status, Combination Strategies, Limitations and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 3;25(9):5007. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095007. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dock G. The influence of complicating diseases upon leukemia. Am J Med Sci. 1904;127:563.
-
- Liu TC, Galanis E, Kirn D. Clinical trial results with oncolytic virotherapy: a century of promise, a decade of progress. Nature clinical practice Oncology. 2007 Feb;4:101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

