TRPA1 mediated aggravation of allergic contact dermatitis induced by DINP and regulated by NF-κB activation
- PMID: 28240277
- PMCID: PMC5327402
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43586
TRPA1 mediated aggravation of allergic contact dermatitis induced by DINP and regulated by NF-κB activation
Abstract
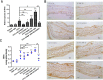
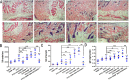
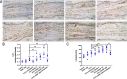
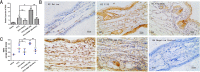
The possible pathogenic role and mechanism of Di-iso-nonyl phthalate (DINP) in allergic dermatitis is still controversial. This work has shown that oral exposure to DINP exacerbated allergic dermatitis tissue lesions in FITC-sensitized mice. The lesions was accompanied by an enhancement of TRPA1 expression and an increase in IgG1, IL-6 and IL-13 levels. This work also found that blocking TRPA1 by HC030031 effectively prevented the development of allergic dermatitis resulting from oral exposure to DINP and/or FITC-sensitized mice. This result is marked by the down regulation of IgG1 levels, a reduction in mast cell degranulation and a decrease in IL-6 and IL-13 levels. We also showed that blocking NF-κB inhibited TRPA1 expression, and that blocking TRPA1 had no significant effect on the activation of NF-κB or TSLP expression. This study helps in understanding the role DINP exposure plays in the development of allergic dermatitis and provides new insight into the mechanisms behind the DINP-induced adjuvant effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diisononyl phthalate aggravates allergic dermatitis by activation of NF-kB.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85472-85482. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13403. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27863430 Free PMC article.
-
Oral exposure to diisodecyl phthalate aggravates allergic dermatitis by oxidative stress and enhancement of thymic stromal lymphopoietin.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Jan;99:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.016. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27871981
-
Exposure to formaldehyde and diisononyl phthalate exacerbate neuroinflammation through NF-κB activation in a mouse asthma model.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Nov 15;163:356-364. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.089. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 30059880
-
Exposure to diisononyl phthalate promotes atopic march by activating of NF-κB and p38 MAPK.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 May 15;395:114981. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.114981. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32240662
-
TRPA1 Expression and Pathophysiology in Immune Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 24;22(21):11460. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111460. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768891 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation-the role of TRPA1 channel.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1093925. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1093925. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36875034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal Regulation of Cutaneous Immunity.J Immunol. 2020 Jan 15;204(2):264-270. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901109. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31907268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update of the risk assessment of di-butylphthalate (DBP), butyl-benzyl-phthalate (BBP), bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP), di-isononylphthalate (DINP) and di-isodecylphthalate (DIDP) for use in food contact materials.EFSA J. 2019 Dec 11;17(12):e05838. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5838. eCollection 2019 Dec. EFSA J. 2019. PMID: 32626195 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomechanisms of Contact Sensitization.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017 Nov 11;17(12):83. doi: 10.1007/s11882-017-0752-8. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017. PMID: 29129023 Review.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)-An Inflammation-Induced Factor in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3322. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073322. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benning J. L., Liu Z., Tiwari A., Little J. C. & Marr L. C. Characterizing gas-particle interactions of phthalate plasticizer emitted from vinyl flooring. Environ Sci Technol 47, 2696–2703 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Zeng Q. et al.. Approach to distribution and accumulation of dibutyl phthalate in rats by immunoassay. Food Chem Toxicol 56, 18–27 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Min A., Liu F., Yang X. & Chen M. Benzyl butyl phthalate exposure impairs learning and memory and attenuates neurotransmission and CREB phosphorylation in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 71, 81–89 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kransler K. M., Bachman A. N. & McKee R. H. A comprehensive review of intake estimates of di-isononyl phthalate (DINP) based on indirect exposure models and urinary biomonitoring data. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 62, 248–256 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Shea K. M. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Environmental H. Pediatric exposure and potential toxicity of phthalate plasticizers. Pediatrics 111, 1467–1474 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

