Water-Insoluble Photosensitizer Nanocolloids Stabilized by Supramolecular Interfacial Assembly towards Photodynamic Therapy
- PMID: 28230203
- PMCID: PMC5322353
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42978
Water-Insoluble Photosensitizer Nanocolloids Stabilized by Supramolecular Interfacial Assembly towards Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
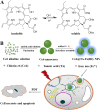
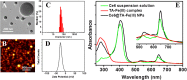
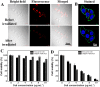
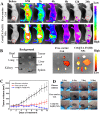
Nanoengineering of hydrophobic photosensitizers (PSs) is a promising approach for improved tumor delivery and enhanced photodynamic therapy (PDT) efficiency. A variety of delivery carriers have been developed for tumor delivery of PSs through the enhanced permeation and retention (EPR) effect. However, a high-performance PS delivery system with minimum use of carrier materials with excellent biocompatibility is highly appreciated. In this work, we utilized the spatiotemporal interfacial adhesion and assembly of supramolecular coordination to achieve the nanoengineering of water-insoluble photosensitizer Chlorin e6 (Ce6). The hydrophobic Ce6 nanoparticles are well stabilized in a aqueous medium by the interfacially-assembled film due to the coordination polymerization of tannic acid (TA) and ferric iron (Fe(III)). The resulting Ce6@TA-Fe(III) complex nanoparticles (referenced as Ce6@TA-Fe(III) NPs) significantly improves the drug loading content (~65%) and have an average size of 60 nm. The Ce6@TA-Fe(III) NPs are almost non-emissive as the aggregated states, but they can light up after intracellular internalization, which thus realizes low dark toxicity and excellent phototoxicity under laser irradiation. The Ce6@TA-Fe(III) NPs prolong blood circulation, promote tumor-selective accumulation of PSs, and enhanced antitumor efficacy in comparison to the free-carrier Ce6 in vivo evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ce6-Modified Carbon Dots for Multimodal-Imaging-Guided and Single-NIR-Laser-Triggered Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy by Reduced Irradiation Power.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Feb 13;11(6):5791-5803. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b19042. Epub 2019 Jan 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30648846
-
Beta-carotene-bound albumin nanoparticles modified with chlorin e6 for breast tumor ablation based on photodynamic therapy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Nov 1;171:123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 30025374
-
Self-Amplified pH/ROS Dual-Responsive Co-Delivery Nano-System with Chemo-Photodynamic Combination Therapy in Hepatic Carcinoma Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Apr 24;19:3737-3751. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S453199. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38699684 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Effect of Photodynamic Therapy/Sonodynamic Therapy/Sono-Photodynamic Therapy of Chlorin e6 and Other Applications.Mol Pharm. 2023 Feb 6;20(2):875-885. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00824. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36689197 Review.
-
Self-Assembled Porphyrinoids: One-Component Nanostructured Photomedicines.ChemMedChem. 2021 Aug 19;16(16):2441-2451. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100201. Epub 2021 May 19. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33900022 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Delivery of Chlorin e6 via Redox Sensitive Diselenide-Containing Micelles for Improved Photodynamic Therapy in Cluster of Differentiation 44-Overexpressing Breast Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Apr 16;10:369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00369. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31057402 Free PMC article.
-
Supramolecular dye nanoassemblies for advanced diagnostics and therapies.Bioeng Transl Med. 2024 Feb 13;9(4):e10652. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10652. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39036081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-pot synthesis chlorin e6 nano-precipitation for colorectal cancer treatment Ce6 NPs for colorectal cancer treatment.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021 Oct;15(8):680-685. doi: 10.1049/nbt2.12065. Epub 2021 Jul 21. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34694720 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and Self-Assembly Behavior of BPEF and BBPEF Composite Langmuir-Blodgett Films with Photovoltaic Conversion Properties.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Sep 18;14(18):1514. doi: 10.3390/nano14181514. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330670 Free PMC article.
-
Iron(III)-Tannic Molecular Nanoparticles Enhance Autophagy effect and T1 MRI Contrast in Liver Cell Lines.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 27;8(1):6647. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25108-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29703912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dolmans D. E., Fukumura D. & Jain R. K. Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 380–387 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Henderson B. W. & Dougherty T. J. How Does Photodynamic Therapy Work? Photochem. photobiol. 55, 145–157 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Lucky S. S., Soo K. C. & Zhang Y. Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Rev. 115, 1990–2042 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

