Differentially expressed proteins underlying childhood cortical dysplasia with epilepsy identified by iTRAQ proteomic profiling
- PMID: 28222113
- PMCID: PMC5319751
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172214
Differentially expressed proteins underlying childhood cortical dysplasia with epilepsy identified by iTRAQ proteomic profiling
Abstract
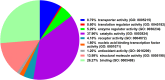
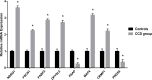
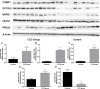
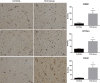
Cortical dysplasia accounts for at least 14% of epilepsy cases, and is mostly seen in children. However, the understanding of molecular mechanisms and pathogenesis underlying cortical dysplasia is limited. The aim of this cross-sectional study is to identify potential key molecules in the mechanisms of cortical dysplasia by screening the proteins expressed in brain tissues of childhood cortical dysplasia patients with epilepsy using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation-based tandem mass spectrometry compared to controls, and several differentially expressed proteins that are not reported to be associated with cortical dysplasia previously were selected for validation using real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. 153 out of 3340 proteins were identified differentially expressed between childhood cortical dysplasia patients and controls. And FSCN1, CRMP1, NDRG1, DPYSL5, MAP4, and FABP3 were selected for validation and identified to be increased in childhood cortical dysplasia patients, while PRDX6 and PSAP were identified decreased. This is the first report on differentially expressed proteins in childhood cortical dysplasia. We identified differential expression of FSCN1, CRMP1, NDRG1, DPYSL5, MAP4, FABP3, PRDX6 and PSAP in childhood cortical dysplasia patients, these proteins are involved in various processes and have various function. These results may provide new directions or targets for the research of childhood cortical dysplasia, and may be helpful in revealing molecular mechanisms and pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology of childhood cortical dysplasia if further investigated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eight further individuals with intellectual disability and epilepsy carrying bi-allelic CNTNAP2 aberrations allow delineation of the mutational and phenotypic spectrum.J Med Genet. 2016 Dec;53(12):820-827. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103880. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 27439707
-
PI3K/AKT pathway mutations cause a spectrum of brain malformations from megalencephaly to focal cortical dysplasia.Brain. 2015 Jun;138(Pt 6):1613-28. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv045. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25722288 Free PMC article.
-
Isobaric labeling and tandem mass spectrometry: a novel approach for profiling and quantifying proteins differentially expressed in amniotic fluid in preterm labor with and without intra-amniotic infection/inflammation.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Apr;23(4):261-80. doi: 10.3109/14767050903067386. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010. PMID: 19670042 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of GATOR complex genes in familial focal epilepsies and focal cortical dysplasia.Epilepsia. 2016 Jun;57(6):994-1003. doi: 10.1111/epi.13391. Epub 2016 May 13. Epilepsia. 2016. PMID: 27173016
-
Electro-clinical-pathological correlations in focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) at young ages.Childs Nerv Syst. 2014 Dec;30(12):2015-26. doi: 10.1007/s00381-014-2549-6. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014. PMID: 25255773 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping the landscape of tandem repeat variability by targeted long read single molecule sequencing in familial X-linked intellectual disability.BMC Med Genomics. 2018 Dec 19;11(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0446-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30567555 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry as a Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Tool for the Search for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Biomarkers: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 5;24(13):11130. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311130. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation in a spectrum of epileptogenic cortical malformations: molecular insights into their interdependence.Brain Pathol. 2019 May;29(3):351-365. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12661. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Brain Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30303592 Free PMC article.
-
Proteogenomics Reveals Orthologous Alternatively Spliced Proteoforms in the Same Human and Mouse Brain Regions with Differential Abundance in an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.Cells. 2021 Jun 23;10(7):1583. doi: 10.3390/cells10071583. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34201730 Free PMC article.
-
Serum biomarkers in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy: a proteomics-based analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Mar 22;15:1383023. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1383023. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38585359 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

