Human parvovirus 4 'PARV4' remains elusive despite a decade of study
- PMID: 28184291
- PMCID: PMC5288687
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.9828.1
Human parvovirus 4 'PARV4' remains elusive despite a decade of study
Abstract
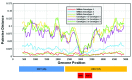
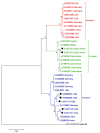
Human parvovirus 4 ('PARV4') is a small DNA tetraparvovirus, first reported in 2005. In some populations, PARV4 infection is uncommon, and evidence of exposure is found only in individuals with risk factors for parenteral infection who are infected with other blood-borne viruses. In other settings, seroprevalence studies suggest an endemic, age-associated transmission pattern, independent of any specific risk factors. The clinical impact of PARV4 infection remains uncertain, but reported disease associations include an influenza-like syndrome, encephalitis, acceleration of HIV disease, and foetal hydrops. In this review, we set out to report progress updates from the recent literature, focusing on the investigation of cohorts in different geographical settings, now including insights from Asia, the Middle East, and South America, and discussing whether attributes of viral or host populations underpin the striking differences in epidemiology. We review progress in understanding viral phylogeny and biology, approaches to diagnostics, and insights that might be gained from studies of closely related animal pathogens. Crucial questions about pathogenicity remain unanswered, but we highlight new evidence supporting a possible link between PARV4 and an encephalitis syndrome. The unequivocal evidence that PARV4 is endemic in certain populations should drive ongoing research efforts to understand risk factors and routes of transmission and to gain new insights into the impact of this virus on human health.
Keywords: Human parvovirus 4; PARV4; PARV4 biology; PARV4 phylogeny; tetraparvovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed. No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

