Podoplanin promotes progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma by regulating motility and focus formation
- PMID: 28182302
- PMCID: PMC5406599
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13190
Podoplanin promotes progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma by regulating motility and focus formation
Abstract
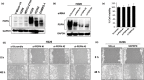
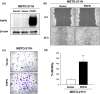
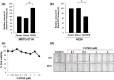
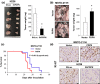
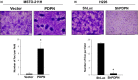
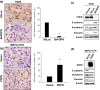
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is characterized by dissemination and aggressive growth in the thoracic cavity. Podoplanin (PDPN) is an established diagnostic marker for MPM, but the function of PDPN in MPM is not fully understood. The purpose of this study was to determine the pathogenetic function of PDPN in MPM. Forty-seven of 52 tumors (90%) from Japanese patients with MPM and 3/6 (50%) MPM cell lines tested positive for PDPN. Knocking down PDPN in PDPN-high expressing MPM cells resulted in decreased cell motility. In contrast, overexpression of PDPN in PDPN-low expressing MPM cells enhanced cell motility. PDPN stimulated motility was mediated by activation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Moreover, knocking down PDPN with short hairpin (sh) RNA in PDPN-high expressing MPM cells resulted in decreased development of a thoracic tumor in mice with severe combined immune deficiency (SCID). In sharp contrast, transfection of PDPN in PDPN-low expressing MPM cells resulted in an increase in the number of Ki-67-positive proliferating tumor cells and it promoted progression of a thoracic tumor in SCID mice. Interestingly, PDPN promoted focus formation in vitro, and a low level of E-cadherin expression and YAP1 activation was observed in PDPN-high MPM tumors. These findings indicate that PDPN is a diagnostic marker as well as a pathogenetic regulator that promotes MPM progression by increasing cell motility and inducing focus formation. Therefore, PDPN might be a pathogenetic determinant of MPM dissemination and aggressive growth and may thus be an ideal therapeutic target.
Keywords: YAP1; focus formation; mesothelioma; motility; podoplanin.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1198-205. doi: 10.1111/cas.12985. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27294401 Free PMC article.
-
GAS5 long non-coding RNA in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 23;13:119. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-119. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885398 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analysis of the Adrenomedullin Pathway in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.J Thorac Oncol. 2016 Jan;11(1):94-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.004. J Thorac Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26762744
-
Podoplanin: An emerging cancer biomarker and therapeutic target.Cancer Sci. 2018 May;109(5):1292-1299. doi: 10.1111/cas.13580. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29575529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Podoplanin in Malignant Progression of Tumor.Cells. 2022 Feb 7;11(3):575. doi: 10.3390/cells11030575. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of a Highly Specific and Sensitive Podoplanin/D2-40, Calretinin, Thyroid Transcription Factor-1, and Carcinoembryonic Antigen/CD66e Immunohistochemical Panel in Differentiating Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma from Metastatic Adenocarcinoma: An Egyptian Experience.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022 Nov 14;12(3):120-125. doi: 10.4103/jmau.jmau_51_22. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022. PMID: 39507645 Free PMC article.
-
Heterocellular N-cadherin junctions enable nontransformed cells to inhibit the growth of adjacent transformed cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Feb 17;20(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00817-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35177067 Free PMC article.
-
Podoplanin, a Potential Therapeutic Target for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 20;2019:7457013. doi: 10.1155/2019/7457013. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31321241 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics and Functional Genomics of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;21(17):6342. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176342. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32882916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Podoplanin promotes cell proliferation, survival, and migration of canine non-tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Oct 18;85(10):1068-1073. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0062. Epub 2023 Aug 4. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37544715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kato Y, Fujita N, Kunita A et al Molecular identification of Aggrus/T1alpha as a platelet aggregation‐inducing factor expressed in colorectal tumors. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 51599–605. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki‐Inoue K, Kato Y, Inoue O et al Involvement of the snake toxin receptor CLEC‐2, in podoplanin –mediated platelet activation, by cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 25993–6001. - PubMed
-
- Fujita N, Takagi S. The impact of Aggrus/podoplanin on platelet aggregation and tumour metastasis. J Biochem 2012; 152: 407–13. - PubMed
-
- Martin‐Villar E, Megias D, Castel S, Yurrita MM, Vilaro S, Quintanilla M. Podoplanin binds ERM proteins to activate RhoA and promote epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 2006; 119: 4541–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

