IgA-coated E. coli enriched in Crohn's disease spondyloarthritis promote TH17-dependent inflammation
- PMID: 28179509
- PMCID: PMC6159892
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf9655
IgA-coated E. coli enriched in Crohn's disease spondyloarthritis promote TH17-dependent inflammation
Abstract
Peripheral spondyloarthritis (SpA) is a common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by inflammatory enthesitis, dactylitis, or synovitis of nonaxial joints. However, a mechanistic understanding of the link between intestinal inflammation and SpA has yet to emerge. We evaluated and functionally characterized the fecal microbiome of IBD patients with or without peripheral SpA. Coupling the sorting of immunoglobulin A (IgA)-coated microbiota with 16S ribosomal RNA-based analysis (IgA-seq) revealed a selective enrichment in IgA-coated Escherichia coli in patients with Crohn's disease-associated SpA (CD-SpA) compared to CD alone. E. coli isolates from CD-SpA-derived IgA-coated bacteria were similar in genotype and phenotype to an adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) pathotype. In comparison to non-AIEC E. coli, colonization of germ-free mice with CD-SpA E. coli isolates induced T helper 17 cell (TH17) mucosal immunity, which required the virulence-associated metabolic enzyme propanediol dehydratase (pduC). Modeling the increase in mucosal and systemic TH17 immunity we observed in CD-SpA patients, colonization of interleukin-10-deficient or K/BxN mice with CD-SpA-derived E. coli lead to more severe colitis or inflammatory arthritis, respectively. Collectively, these data reveal the power of IgA-seq to identify immunoreactive resident pathosymbionts that link mucosal and systemic TH17-dependent inflammation and offer microbial and immunophenotype stratification of CD-SpA that may guide medical and biologic therapy.
Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

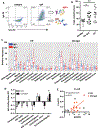
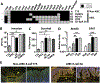
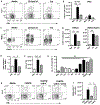
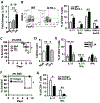
Comment in
-
Spondyloarthropathies: E. coli links IBD to spondyloarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Apr;13(4):198. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.26. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28228648 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Adherent-invasive E. coli metabolism of propanediol in Crohn's disease regulates phagocytes to drive intestinal inflammation.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Apr 14;29(4):607-619.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 33539767 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-associated adherent-invasive Escherichia coli are enriched in pathways for use of propanediol and iron and M-cell translocation.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014 Nov;20(11):1919-32. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000183. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014. PMID: 25230163
-
Siderophore Immunization Restricted Colonization of Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli and Ameliorated Experimental Colitis.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0218422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02184-22. Epub 2022 Sep 12. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36094114 Free PMC article.
-
Italian Expert Panel on the management of patients with coexisting spondyloarthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Aug;13(8):822-30. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24726868 Review.
-
Escherichia coli-host macrophage interactions in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):8751-63. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short Chain Fatty Acids Modulate the Growth and Virulence of Pathosymbiont Escherichia coli and Host Response.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;9(8):462. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080462. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751519 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Complexity Browser: Visualization and quantification of genome variability.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Oct 9;16(10):e1008222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008222. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 33035207 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota Modulation on Intestinal Mucosal Adaptive Immunity.J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 3;2019:4735040. doi: 10.1155/2019/4735040. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31687412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interspecies commensal interactions have nonlinear impacts on host immunity.Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Jul 13;30(7):988-1002.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 30. Cell Host Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35640610 Free PMC article.
-
Human Leukocyte Antigen B27-Negative Axial Spondyloarthritis: What Do We Know?ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023 Jul;5(7):333-344. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11555. Epub 2023 May 24. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37222563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeFilippis EM, Longman R, Harbus M, Dannenberg K, Scherl EJ, Crohn’s Disease: Evolution, Epigenetics, and the Emerging Role of Microbiome-Targeted Therapies. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 18, 13 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Longman RS, E., in Medical Therapy of Ulcerative Colitis, Lichtenstein G, Ed. (Springer Science, New York, 2015).
-
- Bargen JA, Complications and sequelae of chronic ulcerative colitis. Ann Intern Med 3, 335–352 (1929).
-
- Mielants H, Veys EM, Devos M, Stefan CC, Goemaere S, Declercq L, Schatteman L, Elewaut D, The Evolution of Spondyloarthropathies in Relation to Gut Histology .1. Clinical Aspects. Journal of Rheumatology 22, 2266–2272 (1995). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

