An unexpected N-terminal loop in PD-1 dominates binding by nivolumab
- PMID: 28165004
- PMCID: PMC5303876
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14369
An unexpected N-terminal loop in PD-1 dominates binding by nivolumab
Abstract
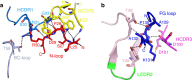
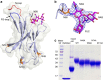
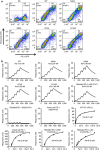
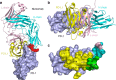
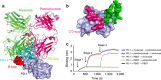
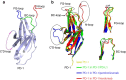
Cancer immunotherapy by targeting of immune checkpoint molecules has been a research 'hot-spot' in recent years. Nivolumab, a human monoclonal antibody targeting PD-1, has been widely used clinically since 2014. However, the binding mechanism of nivolumab to PD-1 has not yet been shown, despite a recent report describing the complex structure of pembrolizumab/PD-1. It has previously been speculated that PD-1 glycosylation is involved in nivolumab recognition. Here we report the complex structure of nivolumab with PD-1 and evaluate the effects of PD-1 N-glycosylation on the interactions with nivolumab. Structural and functional analyses unexpectedly reveal an N-terminal loop outside the IgV domain of PD-1. This loop is not involved in recognition of PD-L1 but dominates binding to nivolumab, whereas N-glycosylation is not involved in binding at all. Nivolumab binds to a completely different area than pembrolizumab. These results provide the basis for the design of future inhibitory molecules targeting PD-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a monoclonal antibody that targets PD-1 in a manner requiring PD-1 Asn58 glycosylation.Commun Biol. 2019 Oct 25;2:392. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0642-9. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31667366 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Biology of the Immune Checkpoint Receptor PD-1 and Its Ligands PD-L1/PD-L2.Structure. 2017 Aug 1;25(8):1163-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2017.06.011. Structure. 2017. PMID: 28768162 Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of immunotherapies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway for previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019 Oct;142:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31326706
-
Molecular Interactions of Antibody Drugs Targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 in Immuno-Oncology.Molecules. 2019 Mar 26;24(6):1190. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061190. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30917623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dynamics of the immune checkpoint programmed cell death protein I, PD-1: conformational changes of the BC-loop upon binding of the ligand PD-L1 and the monoclonal antibody nivolumab.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Dec 14;21(Suppl 17):557. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03904-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33308148 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Looking for the Optimal PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitor in Cancer Treatment: A Comparison in Basic Structure, Function, and Clinical Practice.Front Immunol. 2020 May 29;11:1088. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01088. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32547566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-12 and PD-1 peptide combination gene therapy for the treatment of melanoma.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jul 16;35(3):102267. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102267. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39176175 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the PD-1 pathway.Sci Adv. 2020 Sep 18;6(38):eabd2712. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd2712. Print 2020 Sep. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32948597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding and molecular basis of the bat coronavirus RaTG13 virus to ACE2 in humans and other species.Cell. 2021 Jun 24;184(13):3438-3451.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.031. Epub 2021 May 24. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34139177 Free PMC article.
-
The Relative Risk of Immune-Related Liver Dysfunction of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Versus Chemotherapy in Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 23;10:1063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01063. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31607917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Couzin-Frankel J. Breakthrough of the year 2013. Cancer immunotherapy. Science 342, 1432–1433 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Gao G. F. et al.. Crystal structure of the complex between human CD8alpha(alpha) and HLA-A2. Nature 387, 630–634 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Gao G. F. & Jakobsen B. K. Molecular interactions of coreceptor CD8 and MHC class I: the molecular basis for functional coordination with the T-cell receptor. Immunol. Today 21, 630–636 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Collins A. V. et al.. The interaction properties of costimulatory molecules revisited. Immunity 17, 201–210 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Bretscher P. & Cohn M. A theory of self-nonself discrimination. Science 169, 1042–1049 (1970). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

