A Brainstem-Spinal Cord Inhibitory Circuit for Mechanical Pain Modulation by GABA and Enkephalins
- PMID: 28162807
- PMCID: PMC7354674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.008
A Brainstem-Spinal Cord Inhibitory Circuit for Mechanical Pain Modulation by GABA and Enkephalins
Abstract
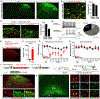
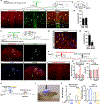
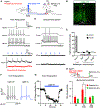
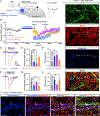
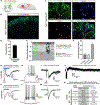
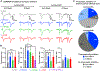
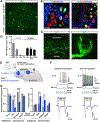
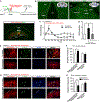
Pain thresholds are, in part, set as a function of emotional and internal states by descending modulation of nociceptive transmission in the spinal cord. Neurons of the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM) are thought to critically contribute to this process; however, the neural circuits and synaptic mechanisms by which distinct populations of RVM neurons facilitate or diminish pain remain elusive. Here we used in vivo opto/chemogenetic manipulations and trans-synaptic tracing of genetically identified dorsal horn and RVM neurons to uncover an RVM-spinal cord-primary afferent circuit controlling pain thresholds. Unexpectedly, we found that RVM GABAergic neurons facilitate mechanical pain by inhibiting dorsal horn enkephalinergic/GABAergic interneurons. We further demonstrate that these interneurons gate sensory inputs and control pain through temporally coordinated enkephalin- and GABA-mediated presynaptic inhibition of somatosensory neurons. Our results uncover a descending disynaptic inhibitory circuit that facilitates mechanical pain, is engaged during stress, and could be targeted to establish higher pain thresholds. VIDEO ABSTRACT.
Keywords: DREADD; GABA; RVM; endogenous opioid enkephalin; in vivo spinal optogenetics; opioid receptors; pain facilitation; presynaptic inhibition; spinal cord; viral circuit tracing.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pain: A gatekeeper circuit.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Apr;18(4):195. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.28. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28228638 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Direct and Indirect Nociceptive Input from the Trigeminal Dorsal Horn to Pain-Modulating Neurons in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla.J Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;43(32):5779-5791. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0680-23.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 24. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37487738 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying local and descending inputs for primary sensory neurons.J Clin Invest. 2015 Oct 1;125(10):3782-94. doi: 10.1172/JCI81156. Epub 2015 Aug 31. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26426077 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting neural circuits from rostral ventromedial medulla to spinal trigeminal nucleus bidirectionally modulating craniofacial mechanical sensitivity.Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Jan;232:102561. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2023.102561. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38142769
-
Presynaptic Inhibition of Pain and Touch in the Spinal Cord: From Receptors to Circuits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 2;22(1):414. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010414. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 'in's and out's' of descending pain modulation from the rostral ventromedial medulla.Trends Neurosci. 2024 Jun;47(6):447-460. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2024.04.006. Epub 2024 May 14. Trends Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38749825 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding of Spinal Wide Dynamic Range Neurons and Their Modulation on Pathological Pain.J Pain Res. 2024 Feb 1;17:441-457. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S446803. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38318328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal cord retinoic acid receptor signaling gates mechanical hypersensitivity in neuropathic pain.Neuron. 2022 Dec 21;110(24):4108-4124.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.09.027. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 36223767 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of bulbospinal ON neurons by GPER, which drives pain and morphine tolerance.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jan 3;133(1):e154588. doi: 10.1172/JCI154588. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 36346677 Free PMC article.
-
An atlas of brain-bone sympathetic neural circuits in mice.Elife. 2024 Jul 4;13:e95727. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95727. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38963696 Free PMC article.
-
A Neural Circuit from Thalamic Paraventricular Nucleus to Central Amygdala for the Facilitation of Neuropathic Pain.J Neurosci. 2020 Oct 7;40(41):7837-7854. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2487-19.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32958568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antal M, Petkó M, Polgár E, Heizmann CW, and Storm-Mathisen J (1996). Direct evidence of an extensive GABAergic innervation of the spinal dorsal horn by fibres descending from the rostral ventromedial medulla. Neuroscience 73, 509–518. - PubMed
-
- Barbaro NM, Heinricher MM, and Fields HL (1986). Putative pain modulating neurons in the rostral ventral medulla: reflex-related activity predicts effects of morphine. Brain Res 366, 203–210. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

