Pharmacokinetics of Clindamycin in Obese and Nonobese Children
- PMID: 28137820
- PMCID: PMC5365720
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02014-16
Pharmacokinetics of Clindamycin in Obese and Nonobese Children
Abstract
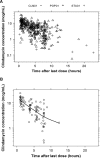
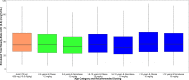
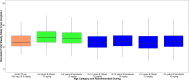
Although obesity is prevalent among children in the United States, pharmacokinetic (PK) data for obese children are limited. Clindamycin is a commonly used antibiotic that may require dose adjustment in obese children due to its lipophilic properties. We performed a clindamycin population PK analysis using data from three separate trials. A total of 420 samples from 220 children, 76 of whom had a body mass index greater than or equal to the 95th percentile for age, were included in the analysis. Compared to other metrics, total body weight (TBW) was the most robust measure of body size. The final model included TBW and a sigmoidal maturation relationship between postmenstrual age (PMA) and clearance (CL): CL (liters/hour) = 13.8 × (TBW/70)0.75 × [PMA2.83/(39.52.83+PMA2.83)]; volume of distribution (V) was associated with TBW, albumin (ALB), and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein (AAG): V (liters) = 63.6 × (TBW/70) × (ALB/3.3)-0.83 × (AAG/2.4)-0.25 After accounting for differences in TBW, obesity status did not explain additional interindividual variability in model parameters. Our findings support TBW-based dosing for obese and nonobese children.
Keywords: antibiotics; children; clindamycin; obesity; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of opportunistic clinical data and a population pharmacokinetic model to support dosing of clindamycin for premature infants to adolescents.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;96(4):429-37. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2014.134. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24949994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Single Bolus Dose Fentanyl in Obese Children.Anesth Analg. 2024 Jan 1;138(1):99-107. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006554. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Anesth Analg. 2024. PMID: 37801572
-
Comparison of Dose Adjustment Strategies for Obesity in High-dose Cyclophosphamide Among Adult Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients: Pharmacokinetic Analysis.Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Dec;28(12):845.e1-845.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.09.011. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 36167308
-
Pediatric Obesity: Pharmacokinetics and Implications for Drug Dosing.Clin Ther. 2015 Sep 1;37(9):1897-923. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.05.495. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 26361823 Review.
-
The relationship between drug clearance and body size: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature published from 2000 to 2007.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 May 1;51(5):319-30. doi: 10.2165/11598930-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22439649 Review.
Cited by
-
Updated antimicrobial dosing recommendations for obese patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 May 2;68(5):e0171923. doi: 10.1128/aac.01719-23. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38526051 Free PMC article.
-
Indomethacin Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Pregnancies With Preterm Labor: The Need for Dose-Ranging Trials.J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;64(6):728-736. doi: 10.1002/jcph.2412. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38315120
-
Impact of Antibiotic-Loaded PMMA Spacers on the Osteogenic Potential of hMSCs.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jan 3;13(1):44. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13010044. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247603 Free PMC article.
-
Product Labeling of Drugs Commonly Administered to Children and Adults with Obesity.Pharm Regul Aff. 2019;8(1):219. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Pharm Regul Aff. 2019. PMID: 37220561 Free PMC article.
-
Effective or Harmful-Evaluation of Locally Applied Antibiotics on Adipose Tissue during Lipofilling to the Breast-An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 24;24(3):2323. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032323. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harskamp-van Ginkel MW, Hill KD, Becker KC, Testoni D, Cohen-Wolkowiez M, Gonzalez D, Barrett JS, Benjamin DK Jr, Siegel DA, Banks P, Watt KM; Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act—Pediatric Trials Network Administrative Core Committee. 2015. Drug dosing and pharmacokinetics in children with obesity: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr 169:678–685. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez D, Melloni C, Yogev R, Poindexter BB, Mendley SR, Delmore P, Sullivan JE, Autmizguine J, Lewandowski A, Harper B, Watt KM, Lewis KC, Capparelli EV, Benjamin DK Jr, Cohen-Wolkowiez M; Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act—Pediatric Trials Network Administrative Core Committee. 2014. Use of opportunistic clinical data and a population pharmacokinetic model to support dosing of clindamycin for premature infants to adolescents. Clin Pharmacol Ther 96:429–437. doi:10.1038/clpt.2014.134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24 HD058735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD081044/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD083465/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 FD004858/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003I/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R18 FD005292/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- K12 HD047349/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD075891/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201500006C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD076676/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017I/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

