β hydroxybutyrate levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid under ketone body metabolism in rats
- PMID: 28100888
- PMCID: PMC5411304
- DOI: 10.1538/expanim.16-0090
β hydroxybutyrate levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid under ketone body metabolism in rats
Abstract
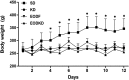
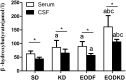
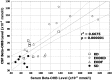
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet (KD) or calorie restriction in the form of every-other-day fasting (EODF) results in ketone body metabolism with an increasing β-hydroxybutyrate (βOHB) level. Previous studies have supported that a KD and EODF have a neuroprotective effect. However, the βOHB levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) resulting from a KD and EODF remain unknown. The aim of this study was to detect βOHB levels in rats fed a KD, EODF diet, and every-other-day ketogenic diet (EODKD) and to compare the serum βOHB level with the CSF βOHB level. Twenty-four male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into KD, EODF, EODKD, and standard diet (SD) groups. A customized food with a ratio of carbohydrates to fats of 1:4 was used in the KD and EODKD groups. The βOHB level was measured using ELISA kits in 200 µl serum and 100 µl CSF samples for each rat after feeding for 2 weeks. The KD, EODF, and EODKD resulted in a significant increase in βOHB levels in both the serum and CSF. The βOHB levels in the EODKD group were the highest. The CSF βOHB level was, on average, 69% of the serum βOHB level. There was a positive correlation between the overall βOHB levels in serum and that in cerebrospinal fluid. This study demonstrated that the KD, EODF, and EODKD resulted in ketone body metabolism, as the βOHB levels increased significantly compared with those resulting from the standard diet. Our results suggested that the serum βOHB level was an indicator of the CSF βOHB level, and that the EODKD was an effective diet to enhance ketogenic metabolism.
Keywords: CSF; ketone dody metabolism; serum; βOHB concentration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ketogenic Metabolism Inhibits Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) and Reduces Oxidative Stress After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Neuroscience. 2017 Dec 16;366:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.09.056. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 29024787
-
Bone microstructure and metabolism changes under the combined intervention of ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting: an in vivo study of rats.Exp Anim. 2019 Aug 14;68(3):371-380. doi: 10.1538/expanim.18-0084. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Exp Anim. 2019. PMID: 30944267 Free PMC article.
-
The Ketone Metabolite β-Hydroxybutyrate Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Spinal Cord Injury by Suppression of Class I Histone Deacetylases.J Neurotrauma. 2017 Sep 15;34(18):2645-2655. doi: 10.1089/neu.2017.5192. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Neurotrauma. 2017. PMID: 28683591
-
Ketone bodies as signaling metabolites.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jan;25(1):42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24140022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate in the Brain: One Molecule, Multiple Mechanisms.Neurochem Res. 2017 Jan;42(1):35-49. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2099-2. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27826689 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of ketogenic diet on some metabolic and non-metabolic diseases: Evidence from human and animal model experiments.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Jan 8;12(3):1444-1464. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3873. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38455178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Action of Ketogenic Diet Treatment: Impact of Decanoic Acid and Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on Sirtuins and Energy Metabolism in Hippocampal Murine Neurons.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 8;12(8):2379. doi: 10.3390/nu12082379. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32784510 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Fasting Protects against Alzheimer's Disease Possible through Restoring Aquaporin-4 Polarity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 29;10:395. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00395. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29238290 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-Responsive Metabolite, β-Hydroxybutyrate, Attenuates Hypertension.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 16;25(3):677-689.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.058. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30332647 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Metabolic Switching and Vascular Cognitive Impairment.J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024 Jun 30;33(2):92-107. doi: 10.7570/jomes24010. Epub 2024 May 13. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38736362 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colombo M., Kruhoeffer M., Gregersen S., Agger A., Jeppesen P., Oerntoft T., Hermansen K.2006. Energy restriction prevents the development of type 2 diabetes in Zucker diabetic fatty rats: coordinated patterns of gene expression for energy metabolism in insulin-sensitive tissues and pancreatic islets determined by oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Metabolism 55: 43–52. - PubMed
-
- de Assis A.M., da Silva J.S., Rech A., Longoni A., Nonose Y., Repond C., de Bittencourt Pasquali M.A., Moreira J.C., Souza D.O., Pellerin L.2016. Cerebral ketone body oxidation is facilitated by a high fat diet enriched with advanced glycation end products in normal and diabetic rats. Front. Neurosci. 10: 509. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00509 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holland A.M., Kephart W.C., Mumford P.W., Mobley C.B., Lowery R.P., Shake J.J., Patel R.K., Healy J.C., McCullough D.J., Kluess H.A., Huggins K.W., Kavazis A.N., Wilson J.M., Roberts M.D.2016. Effects of a ketogenic diet on adipose tissue, liver, and serum biomarkers in sedentary rats and rats that exercised via resisted voluntary wheel running. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 311: R337–R351. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00156.2016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

