Mesenchymal stem cells-seeded bio-ceramic construct for bone regeneration in large critical-size bone defect in rabbit
- PMID: 28096633
- PMCID: PMC5227108
- DOI: 10.46582/jsrm.1202013
Mesenchymal stem cells-seeded bio-ceramic construct for bone regeneration in large critical-size bone defect in rabbit
Abstract
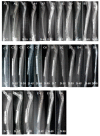
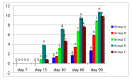
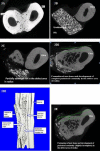
Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC) represent an attractive cell population for tissue engineering purpose. The objective of this study was to determine whether the addition of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP-2) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) to a silica-coated calcium hydroxyapatite (HASi) - rabbit bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell (rBMSC) construct promoted bone healing in a large segmental bone defect beyond standard critical -size radial defects (15mm) in rabbits. An extensively large 30mm long radial ostectomy was performed unilaterally in thirty rabbits divided equally in five groups. Defects were filled with a HASi scaffold only (group B); HASi scaffold seeded with rBMSC (group C); HASi scaffold seeded with rBMSC along with rhBMP-2 and IGF-1 in groups D and E respectively. The same number of rBMSC (five million cells) and concentration of growth factors rhBMP-2 (50µg) and IGF-1 (50µg) was again injected at the site of bone defect after 15 days of surgery in their respective groups. An empty defect served as the control group (group A). Radiographically, bone healing was evaluated at 7, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90 days post implantation. Histological qualitative analysis with microCT (µ-CT), haematoxylin and eosin (H & E) and Masson's trichrome staining were performed 90 days after implantation. All rhBMP-2-added constructs induced the formation of well-differentiated mineralized woven bone surrounding the HASi scaffolds and bridging bone/implant interfaces as early as eight weeks after surgery. Bone regeneration appeared to develop earlier with the rhBMP-2 constructs than with the IGF-1 added construct. Constructs without any rhBMP-2 or IGF-1 showed osteoconductive properties limited to the bone junctions without bone ingrowths within the implantation site. In conclusion, the addition of rhBMP-2 to a HASi scaffold could promote bone generation in a large critical-size-defect.
Keywords: Insulin like growth factor; Mesenchymal stem cells; Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein; Silica-coated calcium.
Similar articles
-
BMP-2 delivered from a self-crosslinkable CaP/hydrogel construct promotes bone regeneration in a critical-size segmental defect model of non-union in dogs.Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2014;27(6):411-21. doi: 10.3415/VCOT-14-03-0036. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2014. PMID: 25327869
-
Novel microhydroxyapatite particles in a collagen scaffold: a bioactive bone void filler?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1318-28. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3438-0. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24385037 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Laden Nanocomposite Scaffolds Enhance Bone Regeneration in Rabbit Critical-Size Segmental Bone Defect Model.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Mar 10;15(3):66. doi: 10.3390/jfb15030066. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38535259 Free PMC article.
-
Periosteum and development of the tissue-engineered periosteum for guided bone regeneration.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Feb 16;33:41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.01.002. eCollection 2022 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 35228996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in biomaterials for long-bone segmental defect reconstruction: A narrative overview.J Orthop Translat. 2019 Oct 8;22:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.09.005. eCollection 2020 May. J Orthop Translat. 2019. PMID: 32440496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-CT - a digital 3D microstructural voyage into scaffolds: a systematic review of the reported methods and results.Biomater Res. 2018 Sep 26;22:26. doi: 10.1186/s40824-018-0136-8. eCollection 2018. Biomater Res. 2018. PMID: 30275969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Defect Repair Using a Bone Substitute Supported by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from the Umbilical Cord.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Apr 5;2020:1321283. doi: 10.1155/2020/1321283. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32300364 Free PMC article.
-
Eco matters; In & Out.J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2016 Nov 29;12(2):52-53. doi: 10.46582/jsrm.1202008. eCollection 2016. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2016. PMID: 28096628 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polydopamine-Laced Biomimetic Material Stimulation of Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Promote Osteogenic Effects.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 11;7(1):12984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13326-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29021583 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of Bone Defect Combined with Massive Loss of Periosteum Using Injectable Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Biocompatible Ceramic Scaffolds in a Porcine Animal Model.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Nov 23;2019:6832952. doi: 10.1155/2019/6832952. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31871469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minier K, Toure A, Fusellier M, Fellah B, Bouvy B, Weiss P, Gauthier O. BMP-2 delivered from a self-cross linkable Ca/P hydrogel construct promotes bone regeneration in a critical-size segmental defect model of non-union in dogs. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2014;27(6):411–21. - PubMed
-
- Kasten P, Vogel J, Luginbuhl R, Niemeyer P, Tonak M, Lorenz H. Ectopic bone formation associated with mesenchymal stem cells in a resorbable calcium deficient hydroxyapatite carrier. Biomaterials. 2005;26(29):5879–89. - PubMed
-
- Bruder SP, Kraus KH, Goldberg VM, Kadiyala S. The effect of implants loaded with autologous mesenchymal stem cells on the healing of canine segmental bone defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(7):985–96. - PubMed
-
- Niemeyer P, Szalay K, Luginbuhl R, Sudkamp NP, Kasten P. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a non-autogenous setting for bone regeneration in a rabbit critical –size-defect model. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(3):900–08. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous