Peroxisomal Dysfunction in Age-Related Diseases
- PMID: 28063767
- PMCID: PMC5366081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.12.003
Peroxisomal Dysfunction in Age-Related Diseases
Abstract
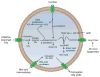
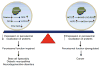
Peroxisomes carry out many key functions related to lipid and reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism. The fundamental importance of peroxisomes for health in humans is underscored by the existence of devastating genetic disorders caused by impaired peroxisomal function or lack of peroxisomes. Emerging studies suggest that peroxisomal function may also be altered with aging and contribute to the pathogenesis of a variety of diseases, including diabetes and its related complications, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. With increasing evidence connecting peroxisomal dysfunction to the pathogenesis of these acquired diseases, the possibility of targeting peroxisomal function in disease prevention or treatment becomes intriguing. Here, we review recent developments in understanding the pathophysiological implications of peroxisomal dysfunctions outside the context of inherited peroxisomal disorders.
Keywords: aging; neurodegeneration; peroxisome; pexophagy; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peroxisomal dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases.Arch Pharm Res. 2019 May;42(5):393-406. doi: 10.1007/s12272-019-01131-2. Epub 2019 Feb 9. Arch Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 30739266 Review.
-
Role of peroxisomes in ROS/RNS-metabolism: implications for human disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1822(9):1363-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22178243 Review.
-
Pro- and Antioxidant Functions of the Peroxisome-Mitochondria Connection and Its Impact on Aging and Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:9860841. doi: 10.1155/2017/9860841. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28811869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisomal Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disease: A Bidirectional Crosstalk.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1299:19-30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-60204-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33417204 Review.
-
Peroxisomal metabolism and oxidative stress.Biochimie. 2014 Mar;98:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.026. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 23933092 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Delivery of Geraniol via Hyaluronic Acid-Conjugation Enhances Its Anti-Tumor Activity Against Prostate Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 6;19:155-169. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S444815. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38204602 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome Proliferator FpPEX11 Is Involved in the Development and Pathogenicity in Fusarium pseudograminearum.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 12;23(20):12184. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012184. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293041 Free PMC article.
-
Edgetic Perturbations Contribute to Phenotypic Variability in PEX26 Deficiency.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 4;12:726174. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.726174. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34804114 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase-deficient mice induce aging faster through lysosomal dysfunction.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Dec 6;20(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00969-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36474295 Free PMC article.
-
Towards early detection of neurodegenerative diseases: A gut feeling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 7;11:1087091. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1087091. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36824371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schrader M, et al. Peroxisome interactions and cross-talk with other subcellular compartments in animal cells. Subcell Biochem. 2013;69:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Waterham HR, Ebberink MS. Genetics and molecular basis of human peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Mol Basis Dis. 2012;1822:1430–1441. - PubMed
-
- Fransen M, et al. Aging, age-related diseases and peroxisomes. In: del Rio LA, editor. Peroxisomes and their Key Role in Cellular Signaling and Metabolism. Springer; 2013. pp. 45–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

