Mechanical stress activates NMDA receptors in the absence of agonists
- PMID: 28045032
- PMCID: PMC5206744
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39610
Mechanical stress activates NMDA receptors in the absence of agonists
Abstract
While studying the physiological response of primary rat astrocytes to fluid shear stress in a model of traumatic brain injury (TBI), we found that shear stress induced Ca2+ entry. The influx was inhibited by MK-801, a specific pore blocker of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR) channels, and this occurred in the absence of agonists. Other NMDA open channel blockers ketamine and memantine showed a similar effect. The competitive glutamate antagonists AP5 and GluN2B-selective inhibitor ifenprodil reduced NMDA-activated currents, but had no effect on the mechanically induced Ca2+ influx. Extracellular Mg2+ at 2 mM did not significantly affect the shear induced Ca2+ influx, but at 10 mM it produced significant inhibition. Patch clamp experiments showed mechanical activation of NMDAR and inhibition by MK-801. The mechanical sensitivity of NMDARs may play a role in the normal physiology of fluid flow in the glymphatic system and it has obvious relevance to TBI.
Figures
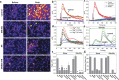
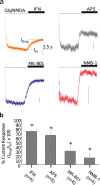
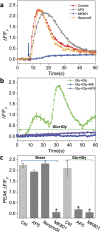
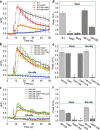
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of in vivo [(3)H]MK-801 binding by NMDA receptor open channel blockers and GluN2B antagonists in rats and mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 5;766:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.044. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26325093
-
A novel method using ambient glutamate for the electrophysiological quantification of extrasynaptic NMDA receptor function in acute brain slices.J Physiol. 2020 Feb;598(4):633-650. doi: 10.1113/JP278362. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31876958
-
Recovery of NMDA receptor currents from MK-801 blockade is accelerated by Mg2+ and memantine under conditions of agonist exposure.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Nov;74:119-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.01.024. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23402996 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor activation contributes to a portion of the decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and elevated intracellular free calcium in strain-injured neurons.J Neurotrauma. 2002 Dec;19(12):1619-29. doi: 10.1089/089771502762300274. J Neurotrauma. 2002. PMID: 12542862
-
The chemical biology of clinically tolerated NMDA receptor antagonists.J Neurochem. 2006 Jun;97(6):1611-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03991.x. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16805772 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in the Pathogenesis of Traumatic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6204. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176204. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Efficacy of Transcranial Focused Ultrasound to the Hippocampus in Alzheimer's Disease: A Preliminary Study.J Pers Med. 2022 Feb 9;12(2):250. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020250. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207738 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Neuron and Glial Cells in Oxidative Injury and Neuroprotection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):13315. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413315. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Going the Extra (Synaptic) Mile: Excitotoxicity as the Road Toward Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Apr 24;14:90. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00090. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32390802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysfunction of the Glymphatic System as a Potential Mechanism of Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jun 7;13:659457. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.659457. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34163349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- MacVicar B. A. Voltage-dependent calcium channels in glial cells. Science (New York, N.Y) 226, 1345–1347 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Rzigalinski B. A., Ellis E. F. & Satin L. S. Reduction of voltage-dependent Mg2+ blockade of NMDA current in mechanically injured neurons. Science (New York, N.Y) 274, 1921–1923 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

