KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs
- PMID: 27899662
- PMCID: PMC5210567
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw1092
KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs
Abstract
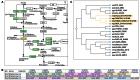
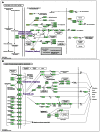
KEGG (http://www.kegg.jp/ or http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) is an encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Assigning functional meanings to genes and genomes both at the molecular and higher levels is the primary objective of the KEGG database project. Molecular-level functions are stored in the KO (KEGG Orthology) database, where each KO is defined as a functional ortholog of genes and proteins. Higher-level functions are represented by networks of molecular interactions, reactions and relations in the forms of KEGG pathway maps, BRITE hierarchies and KEGG modules. In the past the KO database was developed for the purpose of defining nodes of molecular networks, but now the content has been expanded and the quality improved irrespective of whether or not the KOs appear in the three molecular network databases. The newly introduced addendum category of the GENES database is a collection of individual proteins whose functions are experimentally characterized and from which an increasing number of KOs are defined. Furthermore, the DISEASE and DRUG databases have been improved by systematic analysis of drug labels for better integration of diseases and drugs with the KEGG molecular networks. KEGG is moving towards becoming a comprehensive knowledge base for both functional interpretation and practical application of genomic information.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KEGG Bioinformatics Resource for Plant Genomics and Metabolomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1374:55-70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3167-5_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26519400
-
KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D457-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1070. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26476454 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Annotation and Metabolic Reconstruction Using KEGG.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1611:135-145. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7015-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28451977
-
BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences.J Mol Biol. 2016 Feb 22;428(4):726-731. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.11.006. Epub 2015 Nov 14. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26585406 Review.
-
Knowledge-Based Analysis of Protein Interaction Networks in Neurodegenerative Diseases.In: Alzate O, editor. Neuroproteomics. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 9. In: Alzate O, editor. Neuroproteomics. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 9. PMID: 21882442 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Conversion from All-Concentrate to All-Roughage Alters Rumen Bacterial Community Composition and Function in Yak, Cattle-Yak, Tibetan Yellow Cattle and Yellow Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(20):2933. doi: 10.3390/ani14202933. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457862 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of stringent-response reflects nutrient stress induced growth impairment and essential amino acids in different Staphylococcus aureus mutants.Sci Rep. 2021 May 6;11(1):9651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88646-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33958641 Free PMC article.
-
Protein profile of well-differentiated versus un-differentiated human bronchial/tracheal epithelial cells.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 23;6(6):e04243. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04243. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32613119 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Rhodococcus opacus R7 Grown on o-Xylene by RNA-Seq.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 12;11:1808. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01808. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32903390 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfiram in glioma: Literature review of drug repurposing.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:933655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.933655. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

