Selective suppression of antisense transcription by Set2-mediated H3K36 methylation
- PMID: 27892455
- PMCID: PMC5133703
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13610
Selective suppression of antisense transcription by Set2-mediated H3K36 methylation
Abstract
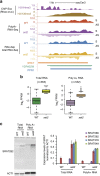
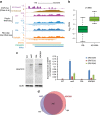
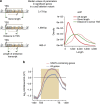
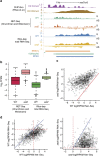
Maintenance of a regular chromatin structure over the coding regions of genes occurs co-transcriptionally via the 'chromatin resetting' pathway. One of the central players in this pathway is the histone methyltransferase Set2. Here we show that the loss of Set2 in yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, results in transcription initiation of antisense RNAs embedded within body of protein-coding genes. These RNAs are distinct from the previously identified non-coding RNAs and cover 11% of the yeast genome. These RNA species have been named Set2-repressed antisense transcripts (SRATs) since the co-transcriptional addition of the H3K36 methyl mark by Set2 over their start sites results in their suppression. Interestingly, loss of chromatin resetting factor Set2 or the subsequent production of SRATs does not affect the abundance of the sense transcripts. This difference in transcriptional outcomes of overlapping transcripts due to a strand-independent addition of H3K36 methylation is a key regulatory feature of interleaved transcriptomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Set2 methylation of histone H3 lysine 36 suppresses histone exchange on transcribed genes.Nature. 2012 Sep 20;489(7416):452-5. doi: 10.1038/nature11326. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22914091
-
XUTs are a class of Xrn1-sensitive antisense regulatory non-coding RNA in yeast.Nature. 2011 Jun 22;475(7354):114-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10118. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21697827
-
Modulation of mRNA and lncRNA expression dynamics by the Set2-Rpd3S pathway.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 28;7:13534. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13534. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27892458 Free PMC article.
-
A site to remember: H3K36 methylation a mark for histone deacetylation.Mutat Res. 2007 May 1;618(1-2):130-4. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.08.014. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Mutat Res. 2007. PMID: 17346757 Review.
-
Memorable transcription.Nat Cell Biol. 2003 May;5(5):390-3. doi: 10.1038/ncb0503-390. Nat Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12724774 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation shapes the transcriptome of quiescent budding yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1043-1063. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1147. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38048329 Free PMC article.
-
BORDER proteins protect expression of neighboring genes by promoting 3' Pol II pausing in plants.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 25;10(1):4359. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12328-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31554790 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Repair in Nucleosomes: Insights from Histone Modifications and Mutants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 16;25(8):4393. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084393. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae model and screen to define the functional consequences of oncogenic histone missense mutations.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 6;12(7):jkac120. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac120. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35567477 Free PMC article.
-
Spt6 Is Required for the Fidelity of Promoter Selection.Mol Cell. 2018 Nov 15;72(4):687-699.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30318445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neil H. et al.. Widespread bidirectional promoters are the major source of cryptic transcripts in yeast. Nature 457, 1038–1042 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

