Identifying Causal Genes at the Multiple Sclerosis Associated Region 6q23 Using Capture Hi-C
- PMID: 27861577
- PMCID: PMC5115837
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166923
Identifying Causal Genes at the Multiple Sclerosis Associated Region 6q23 Using Capture Hi-C
Abstract
Background: The chromosomal region 6q23 has been found to be associated with multiple sclerosis (MS) predisposition through genome wide association studies (GWAS). There are four independent single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with MS in this region, which spans around 2.5 Mb. Most GWAS variants associated with complex traits, including these four MS associated SNPs, are non-coding and their function is currently unknown. However, GWAS variants have been found to be enriched in enhancers and there is evidence that they may be involved in transcriptional regulation of their distant target genes through long range chromatin looping.
Aim: The aim of this work is to identify causal disease genes in the 6q23 locus by studying long range chromatin interactions, using the recently developed Capture Hi-C method in human T and B-cell lines. Interactions involving four independent associations unique to MS, tagged by rs11154801, rs17066096, rs7769192 and rs67297943 were analysed using Capture Hi-C Analysis of Genomic Organisation (CHiCAGO).
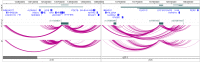
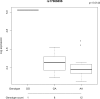
Results: We found that the pattern of chromatin looping interactions in the MS 6q23 associated region is complex. Interactions cluster in two regions, the first involving the rs11154801 region and a second containing the rs17066096, rs7769192 and rs67297943 SNPs. Firstly, SNPs located within the AHI1 gene, tagged by rs11154801, are correlated with expression of AHI1 and interact with its promoter. These SNPs also interact with other potential candidate genes such as SGK1 and BCLAF1. Secondly, the rs17066096, rs7769192 and rs67297943 SNPs interact with each other and with immune-related genes such as IL20RA, IL22RA2, IFNGR1 and TNFAIP3. Finally, the above-mentioned regions interact with each other and therefore, may co-regulate these target genes.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the four 6q23 variants, independently associated with MS, are involved in the regulation of several genes, including immune genes. These findings could help understand mechanisms of disease and suggest potential novel therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
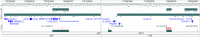
Similar articles
-
Capture Hi-C identifies a novel causal gene, IL20RA, in the pan-autoimmune genetic susceptibility region 6q23.Genome Biol. 2016 Nov 1;17(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1078-x. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27799070 Free PMC article.
-
Functional relevance for multiple sclerosis-associated genetic variants.Immunogenetics. 2015 Jan;67(1):7-14. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0803-4. Epub 2014 Oct 12. Immunogenetics. 2015. PMID: 25308886
-
Enhancer variants associated with Alzheimer's disease affect gene expression via chromatin looping.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Sep 9;12(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0574-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31500627 Free PMC article.
-
The role of non-HLA single nucleotide polymorphisms in multiple sclerosis susceptibility.J Neuroimmunol. 2010 Dec 15;229(1-2):5-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Neuroimmunol. 2010. PMID: 20832869 Review.
-
Reworking GWAS Data to Understand the Role of Nongenetic Factors in MS Etiopathogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 14;11(1):97. doi: 10.3390/genes11010097. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31947683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes.Genome Biol. 2017 Sep 4;18(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1285-0. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28870212 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of LMH cells in response to the overexpression of a protein of Eimeria tenella encoded by the locus ETH_00028350.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 21;9:1053701. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1053701. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36478946 Free PMC article.
-
Primary osteoarthritis chondrocyte map of chromatin conformation reveals novel candidate effector genes.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jul 15;83(8):1048-1059. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224945. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38479789 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Looping Links Target Genes with Genetic Risk Loci for Dermatological Traits.J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Aug;141(8):1975-1984. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.01.015. Epub 2021 Feb 17. J Invest Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33607115 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Rchitect: an R based visualizer for network analysis of chromatin interaction data.Bioinformatics. 2020 Jan 15;36(2):644-646. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz608. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31373608 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

