Spatial buffering of light-evoked potassium increases by retinal Müller (glial) cells
- PMID: 2785716
- PMCID: PMC2562506
- DOI: 10.1126/science.2785716
Spatial buffering of light-evoked potassium increases by retinal Müller (glial) cells
Abstract
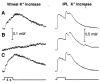
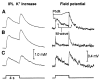
Activity-dependent variations in extracellular potassium concentration in the central nervous system may be regulated, in part, by potassium spatial buffering currents in glial cells. The role of spatial buffering in the retina was assessed by measuring light-evoked potassium changes in amphibian eyecups. The amplitude of potassium increases in the vitreous humor was reduced to approximately 10 percent by 50 micromolar barium, while potassium increases in the inner plexiform layer were largely unchanged. The decrease in the vitreal potassium response was accurately simulated with a numerical model of potassium current flow through Müller cells, the principal glial cells of the retina. Barium also substantially increased the input resistance of Müller cells and blocked the Müller cell-generated M-wave, indicating that barium blocks the potassium channels of Müller cells. Thus, after a light-evoked potassium increase within the retina, there is a substantial transfer of potassium from the retina to the vitreous humor by potassium current flow through Müller cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spatial buffering of extracellular potassium by Müller (glial) cells in the toad retina.Exp Eye Res. 1992 Oct;55(4):539-50. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(05)80166-6. Exp Eye Res. 1992. PMID: 1483500
-
Potassium buffering by Müller cells isolated from the center and periphery of the frog retina.Glia. 1999 Aug;27(2):171-80. Glia. 1999. PMID: 10417816
-
Inward-rectifying potassium channels in retinal glial (Müller) cells.J Neurosci. 1993 Aug;13(8):3333-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-08-03333.1993. J Neurosci. 1993. PMID: 8340811 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular substrates of potassium spatial buffering in glial cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2003 Oct;28(2):195-208. doi: 10.1385/MN:28:2:195. Mol Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14576456 Review.
-
Potassium buffering in the central nervous system.Neuroscience. 2004;129(4):1045-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.008. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15561419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular K+ in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat during reflex bursting activity by oxytocin neurones.J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:383-409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018672. J Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1895242 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental maturation of activity-induced K+ and pH transients and the associated extracellular space dynamics in the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(2):583-597. doi: 10.1113/JP276768. Epub 2018 Nov 24. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30357826 Free PMC article.
-
The astrocyte odyssey.Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Dec 11;86(4):342-67. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.09.015. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18948166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurovascular coupling is not mediated by potassium siphoning from glial cells.J Neurosci. 2007 Mar 7;27(10):2468-71. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3204-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17344384 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Müller Cells in the Diabetic Retinopathy Development: Focus on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;11(4):617. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040617. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Orkand RK, Nicholls JG, Kuffler SW. J Neurophysiol. 1966;29:788. - PubMed
-
- Ransom BR, Carlini WG. In: Astrocytes. Fedoroff S, Vernadakis A, editors. Vol. 2. Academic Press; Orlando: 1986. p. 1.
-
- Gardner-Medwin AR, Nicholson C. J Physiol (London) 1983;335:375. - PMC - PubMed
- Dietzel I, Heine-mann U, Hofmeier G, Lux HD. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40:432. - PubMed
- Gardner-Medwin AR, Coles JA, Tsacopoulos M. Brain Res. 1981;209:452. - PubMed
- Coles JA, Orkand RK. J Physiol (London) 1983;340:157. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karwoski CJ. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1988;37:217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

