Allyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits the Proliferation of Renal Carcinoma Cell Line GRC-1 by Inducing an Imbalance Between Bcl2 and Bax
- PMID: 27834342
- PMCID: PMC5115214
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.897315
Allyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits the Proliferation of Renal Carcinoma Cell Line GRC-1 by Inducing an Imbalance Between Bcl2 and Bax
Abstract
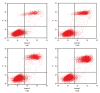
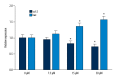
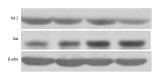
BACKGROUND Because of the insensitivity of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) to both chemotherapy and radiotherapy, surgery remains the primary approach for anticancer treatment. However, patients who do not receive timely diagnoses may not be suitable for surgery, especially in the late phase of tumor development. Thus, the discovery of novel effective treatment is of great importance. Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) can inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis in many cancer cells. In this paper, we report on an in vitro study to determine the effect of AITC on proliferation and apoptosis of RCC line GRC-1. MATERIAL AND METHODS CCK8 assay was used to detect cell proliferation under gradient concentrations of AITC. Flow cytometry was employed to evaluate cell apoptosis. Real-time fluorescent polymerase chain reaction quantified mRNA levels of Bax and Bcl-2 genes. Western blotting was further employed for protein expression assay. RESULTS AITC inhibited GRC-1 cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner; it also elevated Bax while suppressing Bcl-2 gene expression at both mRNA and protein levels. In general, increasing concentration of AITC decreased Bcl-2/Bax ratio. CONCLUSIONS The inhibitory effect of AITC on GRC-1 cells is exerted via cell apoptosis, in which the imbalance of Bcl-2/Bax plays a significant role.
Keywords: Alprenolol; Apoptosis Inducing Factor; Cellulose 1,4-beta-Cellobiosidase.
Conflict of interest statement
of conflict of interest The authors declare no competing financial or commercial interests in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allyl isothiocyanate regulates oxidative stress, inflammation, cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis via interaction with multiple cell signaling pathways.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Mar;161(3):211-221. doi: 10.1007/s00418-023-02255-9. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38019291 Review.
-
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase 1 (MTHFD1) is Underexpressed in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Tissue and Transfection and Overexpression in Caki-1 Cells Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Increases Apoptosis.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 21;24:8391-8400. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911124. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30459299 Free PMC article.
-
[Apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma and apoptotic related genes bcl-2 and bax].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1998 Jun;36(6):373-5. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1998. PMID: 11825416 Chinese.
-
[Effects of matrine on proliferation and apoptosis of human renal cell carcinoma cell line GRC-1].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2006 Jul;4(4):388-91. doi: 10.3736/jcim20060414. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16834977 Chinese.
-
Chemopreventive aspects, investigational anticancer applications and current perspectives on allyl isothiocyanate (AITC): a review.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Dec;478(12):2763-2777. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04697-0. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36929336 Review.
Cited by
-
Allyl isothiocyanate regulates oxidative stress, inflammation, cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis via interaction with multiple cell signaling pathways.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Mar;161(3):211-221. doi: 10.1007/s00418-023-02255-9. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38019291 Review.
-
Peripheral CD4 +CD8 + double positive T cells: A potential marker to evaluate renal impairment susceptibility during systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biomed Res. 2022 Sep 28;37(1):59-68. doi: 10.7555/JBR.36.20220094. Online ahead of print. J Biomed Res. 2022. PMID: 36625011 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of ATP citrate lyase in renal cell carcinoma tissues and its effect on the human renal carcinoma cells in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2018 May;15(5):6967-6974. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8211. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29725424 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Isothiocyanates as Cancer Chemo-Preventive, Chemo-Therapeutic and Anti-Melanoma Agents.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Apr 18;8(4):106. doi: 10.3390/antiox8040106. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31003534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Evaluation of the Anti-Carcinogenic Response of Major Isothiocyanates in Non-Metastatic and Metastatic Melanoma Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 13;10(2):284. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020284. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amato RJ. Renal cell carcinoma: Review of novel single-agent therapeutics and combination regimens. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(1):7–15. - PubMed
-
- Xu K, Thornalley PJ. Studies on the mechanism of the inhibition of human leukaemia cell growth by dietary isothiocyanates and their cysteine adducts in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;60(2):221–31. - PubMed
-
- Xiao D, Srivastava SK, Lew KL, et al. Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables, inhibits proliferation of human prostate cancer cells by causing G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24(5):891–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials