Reprogramming macrophage orientation by microRNA 146b targeting transcription factor IRF5
- PMID: 27825654
- PMCID: PMC5161420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.041
Reprogramming macrophage orientation by microRNA 146b targeting transcription factor IRF5
Abstract
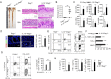
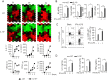
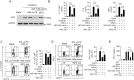
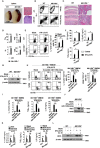
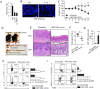
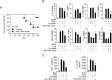
The regulation of macrophage orientation pathological conditions is important but still incompletely understood. Here, we show that IL-10 and Rag1 double knockout mice spontaneously develop colitis with dominant M1 macrophage phenotype, suggesting that IL-10 regulates macrophage orientation in inflammation. We demonstrate that IL-10 stimulation induced miR-146b expression, and that the expression of miR-146b was impaired in IL-10 deficient macrophages. Our data show that miR-146b targets IRF5, resulting in the regulation of macrophage activation. Furthermore, miR-146b deficient mice developed intestinal inflammation with enhanced M1 macrophage polarization. Finally, miR-146b mimic treatment significantly suppresses M1 macrophage activation and ameliorates colitis development in vivo. Collectively, the results suggest that IL-10 dependent miR-146b plays an important role in the modulation of M1 macrophage orientation.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Colitis; Interleukin 10; Macrophage; miR-146b.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Molecular Targeted Immunotherapeutic Strategy for Ulcerative Colitis via Dual-targeting Nanoparticles Delivering miR-146b to Intestinal Macrophages.J Crohns Colitis. 2019 Mar 30;13(4):482-494. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy181. J Crohns Colitis. 2019. PMID: 30445446
-
MicroR-146 blocks the activation of M1 macrophage by targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 in hepatic schistosomiasis.EBioMedicine. 2016 Nov;13:339-347. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.024. Epub 2016 Oct 19. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27780686 Free PMC article.
-
1,25‑Dihydroxyvitamin D regulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease by suppressing miR-125b.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Feb;67:106-118. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30540970
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of non-coding RNAs on macrophage polarization.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;142:112112. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112112. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34449319 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as Regulators of Phagocytosis.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/cells11091380. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust partitioning of microRNA targets from downstream regulatory changes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 25;48(17):9724-9746. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa687. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32821933 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-302a suppresses influenza A virus-stimulated interferon regulatory factor-5 expression and cytokine storm induction.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21291-21303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.805937. Epub 2017 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29046356 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of miRNA in regulating macrophage polarization.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 31;9(11):e21615. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21615. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of miRNAs in Cultured Atlantic Salmon Head Kidney Monocyte-Like and Macrophage-Like Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 2;21(11):3989. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113989. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32498303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S., Misawa T., Satoh T., Saitoh T. Macrophages control innate inflammation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013;15(Suppl. 3):10–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

