Improved Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Marker Gene Primers for Microbial Community Surveys
- PMID: 27822518
- PMCID: PMC5069754
- DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00009-15
Improved Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Marker Gene Primers for Microbial Community Surveys
Abstract
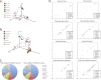
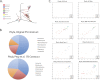
Designing primers for PCR-based taxonomic surveys that amplify a broad range of phylotypes in varied community samples is a difficult challenge, and the comparability of data sets amplified with varied primers requires attention. Here, we examined the performance of modified 16S rRNA gene and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) primers for archaea/bacteria and fungi, respectively, with nonaquatic samples. We moved primer bar codes to the 5' end, allowing for a range of different 3' primer pairings, such as the 515f/926r primer pair, which amplifies variable regions 4 and 5 of the 16S rRNA gene. We additionally demonstrated that modifications to the 515f/806r (variable region 4) 16S primer pair, which improves detection of Thaumarchaeota and clade SAR11 in marine samples, do not degrade performance on taxa already amplified effectively by the original primer set. Alterations to the fungal ITS primers did result in differential but overall improved performance compared to the original primers. In both cases, the improved primers should be widely adopted for amplicon studies. IMPORTANCE We continue to uncover a wealth of information connecting microbes in important ways to human and environmental ecology. As our scientific knowledge and technical abilities improve, the tools used for microbiome surveys can be modified to improve the accuracy of our techniques, ensuring that we can continue to identify groundbreaking connections between microbes and the ecosystems they populate, from ice caps to the human body. It is important to confirm that modifications to these tools do not cause new, detrimental biases that would inhibit the field rather than continue to move it forward. We therefore demonstrated that two recently modified primer pairs that target taxonomically discriminatory regions of bacterial and fungal genomic DNA do not introduce new biases when used on a variety of sample types, from soil to human skin. This confirms the utility of these primers for maintaining currently recommended microbiome research techniques as the state of the art.
Keywords: 16S; ITS; marker genes; microbial ecology; primers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Every base matters: assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples.Environ Microbiol. 2016 May;18(5):1403-14. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13023. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26271760
-
Evaluating and Improving Small Subunit rRNA PCR Primer Coverage for Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes Using Metagenomes from Global Ocean Surveys.mSystems. 2021 Jun 29;6(3):e0056521. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00565-21. Epub 2021 Jun 1. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34060911 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of 16S rRNA primer pairs in identifying nitrifying guilds in soils under long-term organic fertilization and water management.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 15;15:1424795. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1424795. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39077744 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-scale evaluation of two standard 16S rRNA gene amplicon primer pairs for analysis of total prokaryotes and archaeal nitrifiers in differently managed soils.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1140487. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1140487. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36910167 Free PMC article.
-
Specific and effective detection of anammox bacteria using PCR primers targeting the 16S rRNA gene and functional genes.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Sep 10;734:139387. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139387. Epub 2020 May 15. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32460079 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Loneliness and Wisdom With Gut Microbial Diversity and Composition: An Exploratory Study.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Mar 25;12:648475. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.648475. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33841213 Free PMC article.
-
Highly-resolved interannual phytoplankton community dynamics of the coastal Northwest Atlantic.ISME Commun. 2022 Apr 20;2(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s43705-022-00119-2. ISME Commun. 2022. PMID: 37938666 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a versatile tool for studying kinetics of Selenate-Se removal from aqueous solution using a chemostat bioreactor.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 19;10(3):e24914. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24914. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38317929 Free PMC article.
-
Application of machine learning in prediction of Chemotherapy resistant of Ovarian Cancer based on Gut Microbiota.J Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;12(10):2877-2885. doi: 10.7150/jca.46621. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33854588 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection status associates with bacterial community composition in patients and the hospital environment.Microbiome. 2021 Jun 8;9(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01083-0. Microbiome. 2021. PMID: 34103074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apprill A, McNally S, Parsons R, Weber L. 2015. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat Microb Ecol 75:129–137. doi:10.3354/ame01753. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

