The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome
- PMID: 27814521
- PMCID: PMC5127403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027
The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome
Abstract
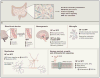
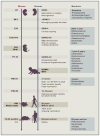
Neurodevelopment is a complex process governed by both intrinsic and extrinsic signals. While historically studied by researching the brain, inputs from the periphery impact many neurological conditions. Indeed, emerging data suggest communication between the gut and the brain in anxiety, depression, cognition, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The development of a healthy, functional brain depends on key pre- and post-natal events that integrate environmental cues, such as molecular signals from the gut. These cues largely originate from the microbiome, the consortium of symbiotic bacteria that reside within all animals. Research over the past few years reveals that the gut microbiome plays a role in basic neurogenerative processes such as the formation of the blood-brain barrier, myelination, neurogenesis, and microglia maturation and also modulates many aspects of animal behavior. Herein, we discuss the biological intersection of neurodevelopment and the microbiome and explore the hypothesis that gut bacteria are integral contributors to development and function of the nervous system and to the balance between mental health and disease.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbiome programming of brain development: implications for neurodevelopmental disorders.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019 Jul;61(7):744-749. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14208. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30868564 Review.
-
Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Neurodevelopmental Impairments: Microbiome, Gut, and Brain Entanglements.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 4;14(10):1254. doi: 10.3390/biom14101254. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the gut microbiome in mediating neurotoxic outcomes to PCB exposure.Neurotoxicology. 2019 Dec;75:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.08.010. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 31454514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: the gut-brain axis.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Mar 1;16(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1434-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30823925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Perturbance of Microbiome and Gut-Brain Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 1;19(8):2251. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082251. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30071612 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between the gut microbiome and fatigue in cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 12;11(1):5847. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84783-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33712647 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota and Bipolar Disorder: An Overview on a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;22(7):3723. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073723. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent alcohol drinking interaction with the gut microbiome: implications for adult alcohol use disorder.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024;4:11881. doi: 10.3389/adar.2024.11881. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024. PMID: 38322648 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Denervation Attenuates Neuroinflammation in the Brain by Regulating Gut-Brain Axis in Rats With Myocardial Infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Apr 26;8:650140. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.650140. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33981735 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic Diets Alter the Gut Microbiome, Resulting in Decreased Susceptibility to and Cognitive Impairment in Rats with Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus.Neurochem Res. 2024 Oct;49(10):2726-2742. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04168-y. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38935224
References
-
- Ait-Belgnaoui A, Durand H, Cartier C, Chaumaz G, Eutamene H, Ferrier L, Houdeau E, Fioramonti J, Bueno L, Theodorou V. Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012;37:1885–1895. - PubMed
-
- Ait-Belgnaoui A, Colom A, Braniste V, Ramalho L, Marrot A, Cartier C, Houdeau E, Theodorou V, Tompkins T. Probiotic gut effect prevents the chronic psychological stress-induced brain activity abnormality in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26:510–520. - PubMed
-
- Alenina N, Klempin F. The role of serotonin in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav Brain Res. 2015;277:49–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

