IL-25 attenuates rheumatoid arthritis through suppression of Th17 immune responses in an IL-13-dependent manner
- PMID: 27812008
- PMCID: PMC5095710
- DOI: 10.1038/srep36002
IL-25 attenuates rheumatoid arthritis through suppression of Th17 immune responses in an IL-13-dependent manner
Abstract
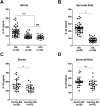
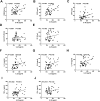
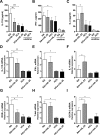
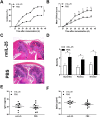
IL-25, a new member of the IL-17 cytokine family, is involved in type 2 immunity initiation and has been associated with the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, its exact role remains unclear. Here, we aimed to analyse IL-25 expression in the serum and synovial fluid of RA patients and evaluated the correlations between serum IL-25 levels, clinical and laboratory values and inflammation cytokines. Additionally, we investigated whether IL-25 can suppress Th1/Th17 responses involved in RA pathogenesis. We further determined whether IL-25 can alleviate collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) development in mice and the underlying mechanisms using in vitro and in vivo experiments. Our results showed that IL-25 was upregulated in the serum and synovial fluid of RA patients. Increased serum IL-25 levels were associated with disease severity and inflammatory response in RA patients. Furthermore, IL-25 inhibited CD4+ T-cell activation and differentiation into Th17 cells, without affecting Th1 cells in human RA and CIA models. Administration of IL-25 could attenuate CIA development by Th17 suppression in an IL-13-dependent manner. Our findings indicate that IL-25 plays a potent immunosuppressive role in the pathogenesis of RA and CIA by downregulating Th17 cell response, and thus, may be a potential therapeutic agent for RA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-37 Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing IL-17 and IL-17-Triggering Cytokine Production and Limiting Th17 Cell Proliferation.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 1;194(11):5110-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401810. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25917106
-
Siglec-9 is upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis and suppresses collagen-induced arthritis through reciprocal regulation of Th17-/Treg-cell differentiation.Scand J Immunol. 2017 Jun;85(6):433-440. doi: 10.1111/sji.12543. Scand J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28273363
-
Sodium Chloride Aggravates Arthritis via Th17 Polarization.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Jan;60(1):88-97. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.1.88. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 30554495 Free PMC article.
-
Effector Functions of CD4+ T Cells at the Site of Local Autoimmune Inflammation-Lessons From Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 12;10:353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00353. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30915067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 27 Signaling in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Good or Evil?Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 4;12:787252. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.787252. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35058928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-25 exacerbates autoimmune aortitis in IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 19;9(1):17067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53633-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31745167 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 2;9:1682. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01682. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30127781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of interleukin-25 in development of spontaneous arthritis in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017 Aug 25;12:62-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.08.006. eCollection 2017 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017. PMID: 28955793 Free PMC article.
-
A novel anti-TNF-α drug ozoralizumab rapidly distributes to inflamed joint tissues in a mouse model of collagen induced arthritis.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 27;12(1):18102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23152-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36302840 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine "fine tuning" of enthesis tissue homeostasis as a pointer to spondyloarthritis pathogenesis with a focus on relevant TNF and IL-17 targeted therapies.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Apr;43(2):193-206. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00836-1. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33544244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fort M. M. et al.. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity 15, 985–995 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Pan G. et al.. Forced expression of murine IL-17E induces growth retardation, jaundice, a Th2-biased response, and multiorgan inflammation in mice. Journal of immunology 167, 6559–6567 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

