Regional variations in fluoroquinolone non-susceptibility among Escherichia coli bloodstream infections within the Veterans Healthcare Administration
- PMID: 27777759
- PMCID: PMC5069952
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-016-0135-2
Regional variations in fluoroquinolone non-susceptibility among Escherichia coli bloodstream infections within the Veterans Healthcare Administration
Abstract
Objectives: We sought to define regional variations in fluoroquinolone non-susceptibility (FQ-NS) among bloodstream isolates of Escherichia coli across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) in the United States.
Methods: We analyzed a retrospective cohort of patients managed at 136 VHA hospitals who had a blood culture positive for E.coli between 2003 and 2013. Hospitals were classified based on US Census Divisions, and regional variations in FQ-NS were analyzed.
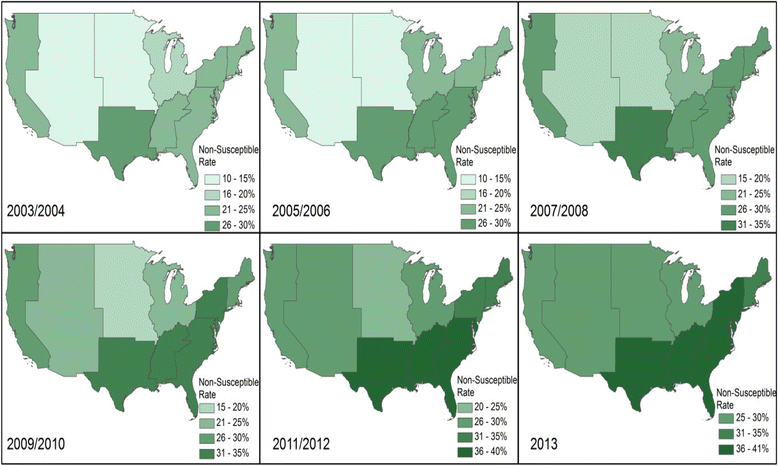
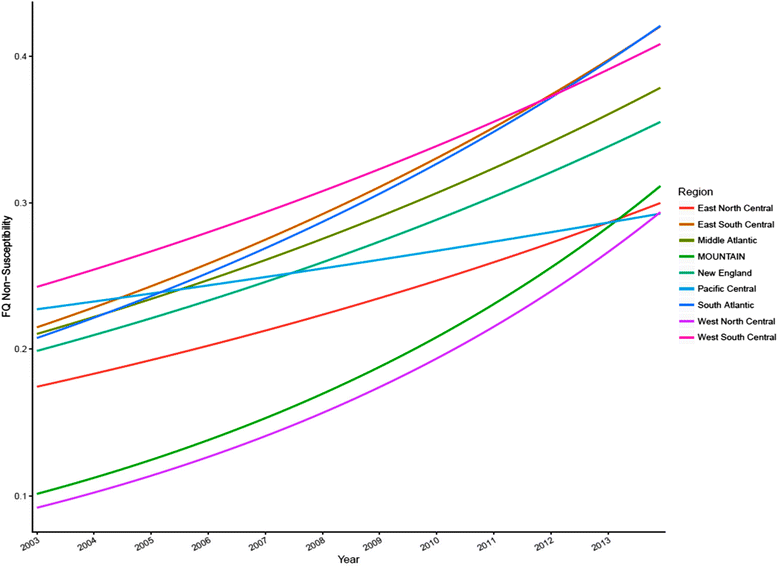
Results: Twenty-four thousand five hundred twenty-three unique E.coli bloodstream infections (BSIs) were identified between 2003 and 2013. 53.9 % of these were community-acquired, 30.7 % were healthcare-associated, and 15.4 % were hospital-onset BSIs. The proportion of E.coli BSIs with FQ-NS significantly varied across US Census Divisions (p < 0.001). During 2003-2013, the proportion of E.coli BSIs with FQ-NS was highest in the West South-Central Division (32.7 %) and lowest in the Mountain Division (20.0 %). Multivariable analysis showed that there were universal secular trends towards higher FQ-NS rates (p < 0.001) with significant variability of slopes across US Census Divisions (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: There has been a universal increase in FQ-NS among E.coli BSIs within VHA, but the rate of increase has significantly varied across Census Divisions. The reasons for this variability are unclear. These findings reinforce the importance of using local data to develop and update local antibiograms and antibiotic-prescribing guidelines.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Epidemiology; Escherichia coli; Fluoroquinolones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of fluoroquinolone resistance in Gram-negative bloodstream infections on healthcare utilization.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015 Sep;21(9):843-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 May 21. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 26003282
-
Escherichia coli sequence type 131 (ST131) subclone H30 as an emergent multidrug-resistant pathogen among US veterans.Clin Infect Dis. 2013 Nov;57(9):1256-65. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit503. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Clin Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23926176 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factor of community-onset spontaneous bacterial peritonitis caused by fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli in patients with cirrhosis.Liver Int. 2014 May;34(5):695-9. doi: 10.1111/liv.12374. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24267669
-
Epidemic Emergence in the United States of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131-H30 (ST131-H30), 2000 to 2009.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jul 25;61(8):e00732-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00732-17. Print 2017 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28533233 Free PMC article.
-
Bloodstream infections in community hospitals in the 21st century: a multicenter cohort study.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 18;9(3):e91713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091713. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24643200 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing the potential for improved predictive capacity of antimicrobial resistance in outpatient Staphylococcus aureus isolates using seasonal and spatial antibiograms.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024 Mar 22;13(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13756-024-01388-3. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2024. PMID: 38519975 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Nonsusceptibility of Gram-Negative Bloodstream Isolates, Veterans Health Administration System, United States, 2003-20131.Emerg Infect Dis. 2017 Nov;23(11):1815-1825. doi: 10.3201/eid2311.161214. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29047423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fasugba O, Gardner A, Mitchell BG, Mnatzaganian G. Ciprofloxacin resistance in community- and hospital-acquired Escherichia coli urinary tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:545. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1282-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zervos MJ, Hershberger E, Nicolau DP, Ritchie DJ, Blackner LK, Coyle EA, Donnelly AJ, Eckel SF, Eng RH, Hiltz A, et al. Relationship between fluoroquinolone use and changes in susceptibility to fluoroquinolones of selected pathogens in 10 United States teaching hospitals, 1991–2000. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(12):1643–1648. doi: 10.1086/379709. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Solomkin JS, Mazuski JE, Bradley JS, Rodvold KA, Goldstein EJ, Baron EJ, O’Neill PJ, Chow AW, Dellinger EP, Eachempati SR, et al. Diagnosis and management of complicated intra-abdominal infection in adults and children: guidelines by the Surgical Infection Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(2):133–164. doi: 10.1086/649554. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG, Moran GJ, Nicolle LE, Raz R, Schaeffer AJ, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(5):e103–e120. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous