Identification of (R)-N-((4-Methoxy-6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-2-methyl-1-(1-(1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-4-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (CPI-1205), a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Histone Methyltransferase EZH2, Suitable for Phase I Clinical Trials for B-Cell Lymphomas
- PMID: 27739677
- PMCID: PMC5451150
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01315
Identification of (R)-N-((4-Methoxy-6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-2-methyl-1-(1-(1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-4-yl)ethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (CPI-1205), a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Histone Methyltransferase EZH2, Suitable for Phase I Clinical Trials for B-Cell Lymphomas
Abstract
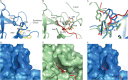
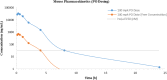
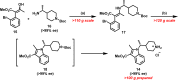
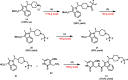
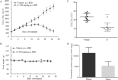
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) has been shown to play a major role in transcriptional silencing in part by installing methylation marks on lysine 27 of histone 3. Dysregulation of PRC2 function correlates with certain malignancies and poor prognosis. EZH2 is the catalytic engine of the PRC2 complex and thus represents a key candidate oncology target for pharmacological intervention. Here we report the optimization of our indole-based EZH2 inhibitor series that led to the identification of CPI-1205, a highly potent (biochemical IC50 = 0.002 μM, cellular EC50 = 0.032 μM) and selective inhibitor of EZH2. This compound demonstrates robust antitumor effects in a Karpas-422 xenograft model when dosed at 160 mg/kg BID and is currently in Phase I clinical trials. Additionally, we disclose the co-crystal structure of our inhibitor series bound to the human PRC2 complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Discovery of IHMT-EZH2-115 as a Potent and Selective Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphomas.J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 28;64(20):15170-15188. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01154. Epub 2021 Oct 19. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34664960
-
Biological evaluation of tanshindiols as EZH2 histone methyltransferase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jun 1;24(11):2486-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.04.010. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24767850
-
Discovery of novel pyridone-benzamide derivatives possessing a 1-methyl-2-benzimidazolinone moiety as potent EZH2 inhibitors for the treatment of B-cell lymphomas.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 May 1;105:117725. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117725. Epub 2024 Apr 14. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38640588
-
Identification of 3-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-2-(1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)propanoic acids as promising DNMT1 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Aug 5;274:116538. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116538. Epub 2024 May 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38823264 Review.
-
Histone methyltransferase inhibitors: novel epigenetic agents for cancer treatment.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(2):167-85. doi: 10.2174/092986713804806667. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23210854 Review.
Cited by
-
EZH2: a novel target for cancer treatment.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jul 28;13(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00937-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32723346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2 and its core component EZH2: potential targeted therapeutic strategies for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Apr 10;16(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01666-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38600608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, mechanism, and regulation of polycomb-repressive complex 2.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 7;293(36):13805-13814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R117.800367. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 28912274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cryptic transactivation domain of EZH2 binds AR and AR's splice variant, promoting oncogene activation and tumorous transformation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 28;50(19):10929-10946. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac861. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36300627 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of IHMT-337 as a potent irreversible EZH2 inhibitor targeting CDK4 transcription for malignancies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jan 16;8(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01240-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36642705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swalm B. M.; Knutson S. K.; Warholic N. M.; Jin L.; Kuntz K. W.; Keilhack H.; Smith J. J.; Pollock R. M.; Moyer M. P.; Scott M. P.; Copeland R. A.; Wigle T. J. Reaction Coupling Between Wild-Type and Disease-Associated Mutant EZH2. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2459–2464. 10.1021/cb500548b. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Varambally S.; Dhanasekaran S. M.; Zhou M.; Barrette T. R.; Kumar-Sinha C.; Sanda M. G.; Ghosh D.; Pienta K. J.; Sewalt R. G.; Otte A. P.; Rubin M. A.; Chinnaiyan A. M. The Polycomb Group Protein EZH2 Is Involved In Progression of Prostate Cancer. Nature 2002, 419, 624–629. 10.1038/nature01075. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

