Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 27718784
- PMCID: PMC5564292
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602252
Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Abstract
Background: Patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck after platinum chemotherapy have a very poor prognosis and limited therapeutic options. Nivolumab, an anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody, was assessed as treatment for this condition.
Methods: In this randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial, we assigned, in a 2:1 ratio, 361 patients with recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck whose disease had progressed within 6 months after platinum-based chemotherapy to receive nivolumab (at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram of body weight) every 2 weeks or standard, single-agent systemic therapy (methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab). The primary end point was overall survival. Additional end points included progression-free survival, rate of objective response, safety, and patient-reported quality of life.
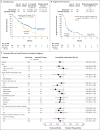
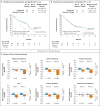
Results: The median overall survival was 7.5 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.5 to 9.1) in the nivolumab group versus 5.1 months (95% CI, 4.0 to 6.0) in the group that received standard therapy. Overall survival was significantly longer with nivolumab than with standard therapy (hazard ratio for death, 0.70; 97.73% CI, 0.51 to 0.96; P=0.01), and the estimates of the 1-year survival rate were approximately 19 percentage points higher with nivolumab than with standard therapy (36.0% vs. 16.6%). The median progression-free survival was 2.0 months (95% CI, 1.9 to 2.1) with nivolumab versus 2.3 months (95% CI, 1.9 to 3.1) with standard therapy (hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.70 to 1.13; P=0.32). The rate of progression-free survival at 6 months was 19.7% with nivolumab versus 9.9% with standard therapy. The response rate was 13.3% in the nivolumab group versus 5.8% in the standard-therapy group. Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in 13.1% of the patients in the nivolumab group versus 35.1% of those in the standard-therapy group. Physical, role, and social functioning was stable in the nivolumab group, whereas it was meaningfully worse in the standard-therapy group.
Conclusions: Among patients with platinum-refractory, recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck, treatment with nivolumab resulted in longer overall survival than treatment with standard, single-agent therapy. (Funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb; CheckMate 141 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02105636 .).
Figures
Comment in
-
Nivolumab for Squamous-Cell Cancer of Head and Neck.N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 9;376(6):596. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1615565. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28177863 No abstract available.
-
Nivolumab for Squamous-Cell Cancer of Head and Neck.N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 9;376(6):595. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1615565. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28181782 No abstract available.
-
Nivolumab for Squamous-Cell Cancer of Head and Neck.N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 9;376(6):595-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1615565. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28181785 No abstract available.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Cancers that Affect the Head and Neck.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017 Aug 1;98(5):969-973. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017. PMID: 28721906 No abstract available.
-
CheckMate 141 trial: all that glitters is not gold.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019 Mar;19(3):169-171. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2019.1570498. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30652499 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nivolumab versus standard, single-agent therapy of investigator's choice in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (CheckMate 141): health-related quality-of-life results from a randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Aug;18(8):1104-1115. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30421-7. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28651929 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 9;373(2):123-35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504627. Epub 2015 May 31. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 26028407 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2015 Oct 22;373(17):1627-39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507643. Epub 2015 Sep 27. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 26412456 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cetuximab for the treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Oct;13 Suppl 3:49-54. doi: 10.3310/hta13suppl3/08. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19846029 Review.
-
Immunotherapy in recurrent and or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Curr Opin Oncol. 2019 May;31(3):146-151. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000522. Curr Opin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30893146 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors Associated with IgG/IgM Levels after SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 8;9(10):234. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9100234. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39453261 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of nivolumab affected by prior cetuximab use and neck dissection in Japanese patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer: results from a retrospective observational study in a real-world setting.Int J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jun;26(6):1049-1056. doi: 10.1007/s10147-021-01900-4. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33830342 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic radiomic expression patterns after 20 Gy demonstrate early metabolic response of oropharyngeal cancers.Med Phys. 2021 Jul;48(7):3767-3777. doi: 10.1002/mp.14926. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33959972 Free PMC article.
-
First-line pembrolizumab ± chemotherapy for recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer: Japanese subgroup of KEYNOTE-048.Int J Clin Oncol. 2022 Dec;27(12):1805-1817. doi: 10.1007/s10147-022-02233-6. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Int J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36264378 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cancer cell-specific PD-L1 expression is a predictor of poor outcome in patients with locally advanced oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Oct 2;12(10):e009617. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009617. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39357980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Pignon JP, le Maître A, Maillard E, Bourhis J. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): an update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Bernier J, Domenge C, Ozsahin M, et al. Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1945–52. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1937–44. - PubMed
-
- Saloura V, Cohen EE, Licitra L, et al. An open-label single-arm, phase II trial of zalutumumab, a human monoclonal anti-EGFR antibody, in patients with platinum-refractory squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73:1227–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
