Fatty liver diseases, bile acids, and FXR
- PMID: 27709009
- PMCID: PMC5045552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.07.008
Fatty liver diseases, bile acids, and FXR
Abstract
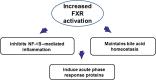
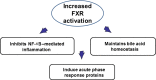
The prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) worldwide has increased at an alarming rate, which will likely result in enormous medical and economic burden. NAFLD presents as a spectrum of liver diseases ranging from simple steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A comprehensive understanding of the mechanism(s) of NAFLD-to-NASH transition remains elusive with various genetic and environmental susceptibility factors possibly involved. An understanding of the mechanism may provide novel strategies in the prevention and treatment to NASH. Abnormal regulation of bile acid homeostasis emerges as an important mechanism to liver injury. The bile acid homeostasis is critically regulated by the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) that is activated by bile acids. FXR has been known to exert tissue-specific effects in regulating bile acid synthesis and transport. Current investigations demonstrate FXR also plays a principle role in regulating lipid metabolism and suppressing inflammation in the liver. Therefore, the future determination of the molecular mechanism by which FXR protects the liver from developing NAFLD may shed light to the prevention and treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: Bile acids; Farnesoid X receptor; Liver lipid metabolism; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of bile acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Mol Aspects Med. 2017 Aug;56:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 May 5. Mol Aspects Med. 2017. PMID: 28442273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic Modulation of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/FGF19 Pathway for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2019;256:325-357. doi: 10.1007/164_2019_228. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31201553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile acid receptors and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.World J Hepatol. 2015 Dec 8;7(28):2811-8. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i28.2811. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26668692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile Acid Nuclear Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: Therapeutic Target for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016 Dec;31(4):500-504. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.500. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016. PMID: 28029021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile acid modulators for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Jun;29(6):623-632. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1763302. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32552182 Review.
Cited by
-
The Farnesoid X Receptor as a Master Regulator of Hepatotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 12;23(22):13967. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213967. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor Klf9 controls bile acid reabsorption and enterohepatic circulation in mice via promoting intestinal Asbt expression.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Sep;43(9):2362-2372. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00850-x. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35105957 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-Acetic Acid Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice via Attenuation of Hepatic Lipogenesis, and Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 3;11(9):2062. doi: 10.3390/nu11092062. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31484323 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Biology and Bile Acid Signalling in Microbiome-Host Interactions in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;10(7):766. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070766. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Mechanisms of Jieduquyuziyin Prescription Improves Lupus Nephritis and Fibrosis via FXR in MRL/lpr Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 9;2022:4301033. doi: 10.1155/2022/4301033. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35855861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Younossi Z.M., Koenig A.B., Abdelatif D., Fazel Y., Henry L., Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Day C.P., James O.F. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842–845. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H., Moschen A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology. 2010;52:1836–1846. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources