Patient's experience with subcutaneous and oral methotrexate for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 27669978
- PMCID: PMC5037591
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1254-x
Patient's experience with subcutaneous and oral methotrexate for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Despite the prominent position of methotrexate (MTX) in Rheumatoid Arthiris (RA) therapeutics, its real-world effectiveness may be influenced by a relative lack of tolerability or other side effects that physicians may not be aware of but that are bothersome to patients. The aim of this study is to identify suboptimal patient experience with MTX and to raise awareness for clinicians to identify opportunities to mitigate bothersome symptoms and side effects and optimize response to MTX.
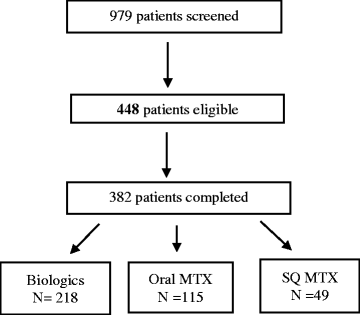
Methods: We conducted a prospective, cross-sectional, online survey among RA patients who were members of Creakyjoints, a large arthritis patient community. Eligible participants must have recently initiated a new biologic, subcutaneous (SQ) MTX, or oral MTX in the last 12 months and were uniquely assigned to one of these 3 groups. Descriptive statistics were used to compare patient-reported side effects and tolerability related to MTX use in the 3 medication groups (SQ MTX, oral MTX, and biologic).
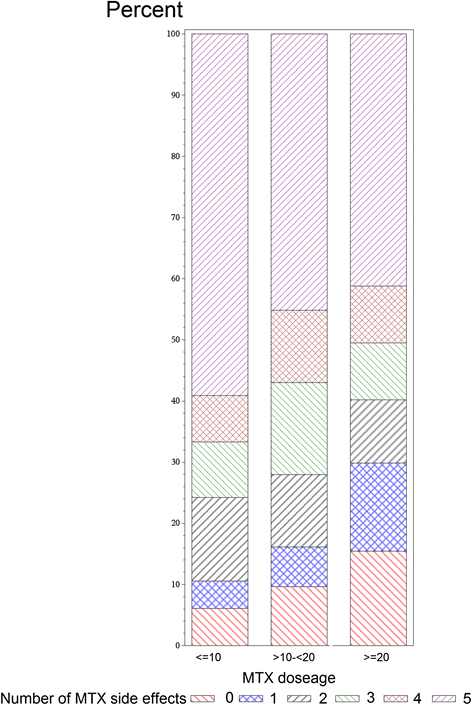
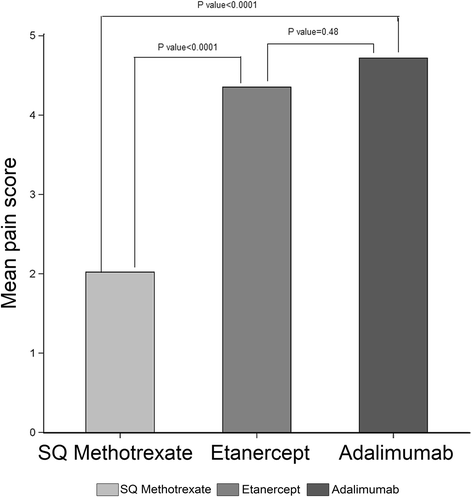
Results: A total of 382 (85 %) of 448 eligible patients completed the survey and were grouped as: biologic (n = 218), SQ MTX (n = 49), and oral MTX (n = 115). Demographics were mean standard deviation (SD) age 48 (10) years, 92 % white, 91 % women. Symptoms significantly more prevalent in the SQ and oral MTX groups included diarrhea, fatigue, malaise, and hair loss. Injection related pain was lower with SQ MTX compared to SQ biologics. Out of a total of 8 potential symptoms and side effects examined, higher dose MTX (> = 20 mg/week) was associated with a 2.26 (1.25-4.09) greater likelihood of more side effects referent to < =10 mg/week.
Conclusion: Results from this real-world RA patient cohort suggest that MTX is accompanied by many patient-reported side effects and tolerability problems that may be under-recognized by physicians. These may impact both treatment satisfaction and medication adherence.
Keywords: Adherence; Methotrexate; Rheumatoid arthritis; Side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness, tolerability, and safety of subcutaneous methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective analysis of real-world data from the St. Gallen cohort.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015 Aug;45(1):28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015. PMID: 25895697
-
Comparative efficacy of subcutaneous versus oral methotrexate in active rheumatoid arthritis.Mymensingh Med J. 2013 Jul;22(3):483-8. Mymensingh Med J. 2013. PMID: 23982537
-
Comparing Healthcare Costs Associated with Oral and Subcutaneous Methotrexate or Biologic Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis in the United States.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017 Feb;10(1):42-49. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017. PMID: 28465768 Free PMC article.
-
Golimumab: Review of the efficacy and tolerability of a recently approved tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor.Clin Ther. 2010 Sep;32(10):1681-703. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.09.003. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 21194591 Review.
-
New autoinjector technology for the delivery of subcutaneous methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014 Sep;11(5):447-55. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2014.929492. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014. PMID: 24934630 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with physicians' prescriptions for rheumatoid arthritis drugs not filled by patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 May 2;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1580-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29720237 Free PMC article.
-
Does concomitant methotrexate confer clinical benefits in patients treated with prior biologic therapy? Analysis of data from a noninterventional study of rheumatoid arthritis patients initiating treatment with adalimumab.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May;99(19):e20201. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020201. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32384515 Free PMC article.
-
Indolent, T-cell, large granular lymphocytic leukaemia in a dog presenting with severe neutropenia and an absence of lymphocytosis.Open Vet J. 2018;8(2):118-124. doi: 10.4314/ovj.v8i2.1. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Open Vet J. 2018. PMID: 29721441 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term use of adalimumab as monotherapy after attainment of low disease activity with adalimumab plus methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.RMD Open. 2018 Jun 13;4(1):e000637. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000637. eCollection 2018. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 29955381 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Adherence to Oral Methotrexate Measured Electronically in Patients With Established Rheumatoid Arthritis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2019 Sep 6;1(9):560-570. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11079. eCollection 2019 Nov. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31777840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Visser K, Katchamart W, Loza E, Martinez-Lopez JA, Salliot C, Trudeau J, Bombardier C, Carmona L, van der Heijde D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Multinational evidence-based recommendations for the use of methotrexate in rheumatic disorders with a focus on rheumatoid arthritis: integrating systematic literature research and expert opinion of a broad international panel of rheumatologists in the 3E Initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(7):1086–93. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.094474. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, Moreland LW, O’Dell J, Winthrop KL, Beukelman T, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64(5):625–39. doi: 10.1002/acr.21641. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gossec L, Nam J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492–509. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nikiphorou E, Negoescu A, Fitzpatrick JD, Goudie CT, Badcock A, Ostor AJ, Malaviya AP. Indispensable or intolerable? Methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: a retrospective review of discontinuation rates from a large UK cohort. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(5):609–14. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2546-x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

