Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Blocks IL1-β-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Chondrocytes by Inducing Autophagy via AKT/mTOR Pathway
- PMID: 27669541
- PMCID: PMC5490987
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.25750
Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Blocks IL1-β-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Chondrocytes by Inducing Autophagy via AKT/mTOR Pathway
Abstract
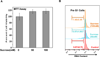
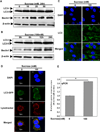
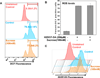
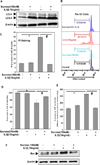
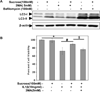
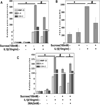
Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) is multifactorial but interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is known to be an important mediator of cartilage degradation. Autophagy is an essential cellular homeostasis mechanism and has been proposed to protect against cartilage degradation and chondrocyte death under pathological conditions. We investigated the role of autophagy activated by sucrose, a natural disaccharide, in suppressing inflammatory mediator's expression and cell death under pathological conditions in human chondrocytes. Autophagy activation was investigated by Western blotting for LC3 and Beclin-1, immunofluorescence staining for LC3 puncta, and measuring autophagic flux. Activation of mTOR, AKT, and P70S6K was evaluated by Western blotting. Chondrocyte apoptosis was evaluated by propidium iodide (PI) staining using flowcytometry, expression of Bax by Western blotting, gene expression by TaqMan assays and caspase 3/7 activity was measured using a luminescence-based assay. We found that sucrose-induced active autophagy in OA chondrocytes in vitro was dependent on the activation of AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways but was independent of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Sucrose activated autophagy blocked IL-1β-induced apoptosis and mRNA expression of MMP-13, COX-2, and IL-6 in human OA chondrocytes. Glucose or fructose, the two metabolites of sucrose, failed to induce autophagy indicating that autophagy was specifically mediated by sucrose. In conclusion, sucrose attenuated IL-1β induced apoptosis and the expression of catabolic mediators by inducing autophagy, and the autophagy in part was mediated through the activation of AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathway in human OA chondrocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 118: 629-639, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: AUTOPHAGY; CHONDROCYTES; OSTEOARTHRITIS; SUCROSE.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Butein Activates Autophagy Through AMPK/TSC2/ULK1/mTOR Pathway to Inhibit IL-6 Expression in IL-1β Stimulated Human Chondrocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(3):932-946. doi: 10.1159/000493225. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30184535
-
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 May;89:1252-1261. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.130. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28320092
-
Silencing UHRF1 enhances cell autophagy to prevent articular chondrocytes from apoptosis in osteoarthritis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Sep 3;529(4):1018-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.032. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32819559
-
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 Apr;28(4):400-409. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.02.027. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 32081707 Review.
-
Saikosaponin D: A potential therapeutic drug for osteoarthritis.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020 Aug;14(8):1175-1184. doi: 10.1002/term.3090. Epub 2020 Jul 7. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32592611 Review.
Cited by
-
pH-sensing G protein-coupled orphan receptor GPR68 is expressed in human cartilage and correlates with degradation of extracellular matrix during OA progression.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 5;11:e16553. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16553. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38077417 Free PMC article.
-
Oroxin B alleviates osteoarthritis through anti-inflammation and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancement of autophagy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 1;13:1060721. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1060721. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36531454 Free PMC article.
-
A proof of concept gene-activated titanium surface for oral implantology applications.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020 Apr;14(4):622-632. doi: 10.1002/term.3026. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32078257 Free PMC article.
-
The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Int Orthop. 2023 Aug;47(8):1895-1919. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05847-1. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Int Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37294429 Review.
-
Up-regulation of P21-activated kinase 1 in osteoarthritis chondrocytes is responsible for osteoarthritic cartilage destruction.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20191017. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191017. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31868209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berenbaum F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!) Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:16–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

