Positive Selection Drives Rapid Evolution of the meq Oncogene of Marek's Disease Virus
- PMID: 27662574
- PMCID: PMC5035050
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162180
Positive Selection Drives Rapid Evolution of the meq Oncogene of Marek's Disease Virus
Abstract
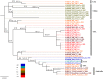
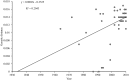
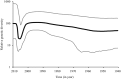
Marek's disease (MD), caused by Marek's disease virus (MDV), a poultry-borne alphaherpesvirus, is a devastating disease of poultry causing an estimated annual loss of one billion dollars to poultry producers, worldwide. Despite decades of control through vaccination, MDV field strains continue to emerge having increased virulence. The evolutionary mechanism driving the emergence of this continuum of strains to increased MDV virulence, however, remains largely enigmatic. Increase in MDV virulence has been associated with specific amino acid changes within the C-terminus domain of Mareks's EcoRI-Q (meq)-encoded oncoprotein. In this study, we sought to determine whether the meq gene has evolved adaptively and whether past vaccination efforts have had any significant effect on the reduction or increase of MDV diversity over time. Our analysis suggests that meq is estimated to be evolving at a much faster rate than most dsDNA viruses, and is comparable with the evolutionary rate of RNA viruses. Interestingly, most of the polymorphisms in meq gene appear to have evolved under positive selection and the time of divergence at the meq locus coincides with the period during which the poultry industry had undergone transitions in management practices including the introduction and widespread use of live attenuated vaccines. Our study has revealed that the decades-long use of vaccines did not reduce MDV diversity, but rather had a stimulating effect on the emergence of field strains with increased genetic diversity until the early 2000s. During the years 2004-2005, there was an abrupt decline in the genetic diversity of field isolates followed by a recovery from this bottleneck in the year 2010. Collectively, these data suggest that vaccination seems to not have had any effect on MDV eradication, but rather had a stimulating effect on MDV emergence through adaptation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors acknowledge no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of Marek's disease virus (MDV) glycoprotein-, lytic antigen pp38- and transformation antigen Meq-encoding genes: association of meq mutations with MDVs of high virulence.Vet Microbiol. 2004 Sep 8;102(3-4):147-67. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.06.007. Vet Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15327791
-
Selection of a recombinant Marek's disease virus in vivo through expression of the Marek's EcoRI-Q (Meq)-encoded oncoprotein: characterization of an rMd5-based mutant expressing the Meq of strain RB-1B.Avian Dis. 2012 Jun;56(2):328-40. doi: 10.1637/9955-100611-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2012. PMID: 22856190
-
Characterization of Meq proteins from field isolates of Marek's disease virus in Japan.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Jun;16:137-43. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.12.032. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23352889
-
Use of Marek's disease vaccines: could they be driving the virus to increasing virulence?Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005 Feb;4(1):77-88. doi: 10.1586/14760584.4.1.77. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005. PMID: 15757475 Review.
-
Successful control of Marek's disease by vaccination.Dev Biol (Basel). 2004;119:147-54. Dev Biol (Basel). 2004. PMID: 15742626 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of the meq oncogene of Marek's disease virus in vaccinated Brazilian poultry farms reveals selective pressure on prevalent strains.Vet Q. 2024 Dec;44(1):1-13. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2318198. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Vet Q. 2024. PMID: 38465827 Free PMC article.
-
Newly detected mutations in the Meq oncogene and molecular pathotyping of very virulent Marek's disease herpesvirus in Tunisia.Arch Virol. 2020 Nov;165(11):2589-2597. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04790-5. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Arch Virol. 2020. PMID: 32876794 Free PMC article.
-
Out of Sight, but Not Out of Mind: Aspects of the Avian Oncogenic Herpesvirus, Marek's Disease Virus.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;10(8):1319. doi: 10.3390/ani10081319. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Insertion and Deletion in the Meq Protein Encoded by Highly Oncogenic Marek's Disease Virus on Transactivation Activity and Virulence.Viruses. 2022 Feb 14;14(2):382. doi: 10.3390/v14020382. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215975 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analyses on Marek's disease virus circulating in Iranian backyard and commercial poultry indicate viruses of different origin.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;53(3):1683-1689. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00738-w. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35484378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shamblin CE, Greene N, Arumugaswami V, Dienglewicz RL, Parcells MS. Comparative analysis of Marek's disease virus (MDV) glycoprotein-, lytic antigen pp38- and transformation antigen Meq-encoding genes: association of meq mutations with MDVs of high virulence. Veterinary microbiology. 2004;102(3–4):147–67. Epub 2004/08/26. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.06.007 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Witter RL. Increased virulence of Marek's disease virus field isolates. Avian diseases. 1997;41(1):149–63. Epub 1997/01/01. . - PubMed
-
- Witter RL. Control strategies for Marek's disease: a perspective for the future. Poultry science. 1998;77(8):1197–203. Epub 1998/08/26. . - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

