An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques
- PMID: 27659679
- PMCID: PMC5036151
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12859
An imbalance between specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and pro-inflammatory leukotrienes promotes instability of atherosclerotic plaques
Abstract
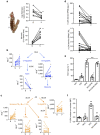
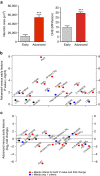
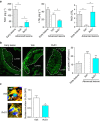
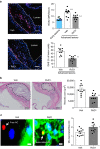
Chronic unresolved inflammation plays a causal role in the development of advanced atherosclerosis, but the mechanisms that prevent resolution in atherosclerosis remain unclear. Here, we use targeted mass spectrometry to identify specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPM) in histologically-defined stable and vulnerable regions of human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. The levels of SPMs, particularly resolvin D1 (RvD1), and the ratio of SPMs to pro-inflammatory leukotriene B4 (LTB4), are significantly decreased in the vulnerable regions. SPMs are also decreased in advanced plaques of fat-fed Ldlr-/- mice. Administration of RvD1 to these mice during plaque progression restores the RvD1:LTB4 ratio to that of less advanced lesions and promotes plaque stability, including decreased lesional oxidative stress and necrosis, improved lesional efferocytosis, and thicker fibrous caps. These findings provide molecular support for the concept that defective inflammation resolution contributes to the formation of clinically dangerous plaques and offer a mechanistic rationale for SPM therapy to promote plaque stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome May be Associated with Decreased Resolvin D1-to-Leukotriene B4 Ratio.Int Heart J. 2023 Mar 31;64(1):22-27. doi: 10.1536/ihj.22-361. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Int Heart J. 2023. PMID: 36682769
-
Resolvin D1 promotes efferocytosis in aging by limiting senescent cell-induced MerTK cleavage.FASEB J. 2020 Jan;34(1):597-609. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902126R. Epub 2019 Nov 26. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31914705 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D1 suppresses macrophage senescence and splenic fibrosis in aged mice.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2024 Mar;202:102634. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2024.102634. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2024. PMID: 39167848
-
The role of non-resolving inflammation in atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2018 Jul 2;128(7):2713-2723. doi: 10.1172/JCI97950. Epub 2018 Jul 2. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30108191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unexpected Role of MPO-Oxidized LDLs in Atherosclerosis: In between Inflammation and Its Resolution.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;11(5):874. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050874. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Specialized pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Nov;21(11):808-823. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00984-x. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38216693 Review.
-
MerTK signaling in macrophages promotes the synthesis of inflammation resolution mediators by suppressing CaMKII activity.Sci Signal. 2018 Sep 25;11(549):eaar3721. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aar3721. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30254055 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus, Silica, and Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Interventions.Toxicol Pathol. 2019 Dec;47(8):1004-1011. doi: 10.1177/0192623319878398. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Toxicol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31725357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages use apoptotic cell-derived methionine and DNMT3A during efferocytosis to promote tissue resolution.Nat Metab. 2022 Apr;4(4):444-457. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00551-7. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Nat Metab. 2022. PMID: 35361955 Free PMC article.
-
The resolution of inflammation through omega-3 fatty acids in atherosclerosis, intimal hyperplasia, and vascular calcification.Semin Immunopathol. 2019 Nov;41(6):757-766. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00767-y. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 31696250 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Viola J. & Soehnlein O. Atherosclerosis—a matter of unresolved inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 27, 184–193 (2015). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

