Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models
- PMID: 27643638
- PMCID: PMC5053891
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4181
Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models
Abstract
Continuous de novo fatty acid synthesis is a common feature of cancer that is required to meet the biosynthetic demands of a growing tumor. This process is controlled by the rate-limiting enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), an attractive but traditionally intractable drug target. Here we provide genetic and pharmacological evidence that in preclinical models ACC is required to maintain the de novo fatty acid synthesis needed for growth and viability of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. We describe the ability of ND-646-an allosteric inhibitor of the ACC enzymes ACC1 and ACC2 that prevents ACC subunit dimerization-to suppress fatty acid synthesis in vitro and in vivo. Chronic ND-646 treatment of xenograft and genetically engineered mouse models of NSCLC inhibited tumor growth. When administered as a single agent or in combination with the standard-of-care drug carboplatin, ND-646 markedly suppressed lung tumor growth in the Kras;Trp53-/- (also known as KRAS p53) and Kras;Stk11-/- (also known as KRAS Lkb1) mouse models of NSCLC. These findings demonstrate that ACC mediates a metabolic liability of NSCLC and that ACC inhibition by ND-646 is detrimental to NSCLC growth, supporting further examination of the use of ACC inhibitors in oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTSJ.G. and S.B. are employed by Schrödinger; G.H., W.F.W., H.J.H., and R.K. are employed by Nimbus Therapeutics.
Figures
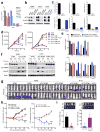
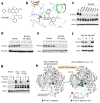
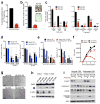
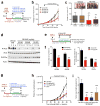
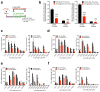
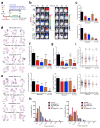
Comment in
-
Blocking fatty acid synthesis reduces lung tumor growth in mice.Nat Med. 2016 Oct 6;22(10):1077-1078. doi: 10.1038/nm.4195. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27711061 No abstract available.
-
Anticancer agents: ACC inhibition suppresses lung cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Nov 3;15(11):750. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.219. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27807350 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and anti-cancer activity of ND-646 and its derivatives as acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 inhibitors.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019 Sep 1;137:105010. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105010. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31325544
-
Gemcitabine and Chk1 Inhibitor AZD7762 Synergistically Suppress the Growth of Lkb1-Deficient Lung Adenocarcinoma.Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 15;77(18):5068-5076. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0567. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28754670 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant LKB1 Confers Enhanced Radiosensitization in Combination with Trametinib in KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 15;24(22):5744-5756. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1489. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30068711
-
Lipid Synthesis Is a Metabolic Liability of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2016;81:93-103. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2016.81.030874. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2016. PMID: 28062532 Review.
-
Targeting KRAS Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Past, Present and Future.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 17;21(12):4325. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124325. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid droplet turnover at the lysosome inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in a BNIP3-dependent manner.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 14;8(41):eabo2510. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo2510. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36223464 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9438. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179438. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273384 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Tuning Lipid Metabolism by Targeting Mitochondria-Associated Acetyl-CoA-Carboxylase 2 in BRAFV600E Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.Thyroid. 2021 Sep;31(9):1335-1358. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0311. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Thyroid. 2021. PMID: 33107403 Free PMC article.
-
TOFA induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ACHN and 786-O cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.J Cancer. 2018 Jun 23;9(15):2734-2742. doi: 10.7150/jca.26374. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30087714 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic R132 IDH1 Mutations Limit NADPH for De Novo Lipogenesis through (D)2-Hydroxyglutarate Production in Fibrosarcoma Sells.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 23;25(4):1018-1026.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.074. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30355481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Kuhajda FP. Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: new perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition. 2000;16:202–208. - PubMed
-
- Menendez JA, Lupu R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:763–777. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

