Electroacupuncture alleviates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via modulation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 27630691
- PMCID: PMC4994450
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.187041
Electroacupuncture alleviates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via modulation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
Abstract
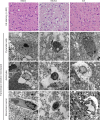
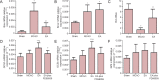
Electroacupuncture (EA) has anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory actions, but whether the neuroprotective effect of EA against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury involves modulation of the extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling pathway is unclear. Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was performed in Sprague-Dawley rats for 2 hours followed by reperfusion for 24 hours. A 30-minute period of EA stimulation was applied to both Baihui (DU20) and Dazhui (DU14) acupoints in each rat (10 mm EA penetration depth, continuous wave with a frequency of 3 Hz, and a current intensity of 1-3 mA) when reperfusion was initiated. EA significantly reduced infarct volume, alleviated neuronal injury, and improved neurological function in rats with MCAO. Furthermore, high mRNA expression of Bax and low mRNA expression of Bcl-2 induced by MCAO was prevented by EA. EA substantially restored total glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels. Additionally, Nrf2 and glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS) expression levels were markedly increased by EA. Interestingly, the neuroprotective effects of EA were attenuated when ERK1/2 activity was blocked by PD98059 (a specific MEK inhibitor). Collectively, our findings indicate that activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway contributes to the neuroprotective effects of EA. Our study provides a better understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effectiveness of EA.
Keywords: B cell lymphoma 2; electroacupuncture; glutamylcysteine synthetase; glutathione peroxidase; glutathione reductase; ischemia and reperfusion injury; middle cerebral artery occlusion; mitogen-activated protein kinase; nerve regeneration; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

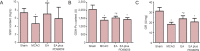
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Mar 7;14:92. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-92. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24606810 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of neuronal zinc finger protein A20 expression is required for electroacupuncture to attenuate the cerebral inflammatory injury mediated by the nuclear factor-kB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Oct 3;13(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0731-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27716383 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at the Baihui (GV20) and Dazhui (GV14) acupoints protects rats against subacute-phase cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injuries by reducing S100B-mediated neurotoxicity.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091426. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24626220 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates nerve injury after cerebra ischemia in rats through inhibiting cell apoptosis and changing the balance of MMP-9/TIMP-1 expression.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Oct 28;633:158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.09.033. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 27664868
-
Electroacupuncture Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion of Rat via Modulation of Apoptosis, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Excitotoxicity.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:9438650. doi: 10.1155/2016/9438650. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27123035 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
2-(2-Benzofuranyl)-2-imidazoline treatment within 5 hours after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion protects the brain.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Dec;13(12):2111-2118. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.241461. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30323139 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture regulates the stress-injury-repair chain of events after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Jun;12(6):925-930. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.208574. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28761425 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 24;2020:7875396. doi: 10.1155/2020/7875396. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33178387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture improves cognitive impairment in diabetic cognitive dysfunction rats by regulating the mitochondrial autophagy pathway.J Physiol Sci. 2022 Nov 22;72(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12576-022-00854-0. J Physiol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36418941 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine Post-Conditioning Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibiting High Mobility Group Protein B1 Group (HMGB1)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jan 8;26:e918617. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918617. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 31912804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen CL, Bayraktutan U. Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2009;4:461–470. - PubMed
-
- Blanquet PR, Mariani J, Fournier B. Temporal assessment of histone H3 phospho-acetylation and casein kinase 2 activation in dentate gyrus from ischemic rats. Brain Res. 2009;1302:10–20. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Simon RP, Nagayama T, Zhu R, Loeffert JE, Watkins SC, Graham SH. Suppression of endogenous bcl-2 expression by antisense treatment exacerbates ischemic neuronal death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1033–1039. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

