The function of heparan sulfate during branching morphogenesis
- PMID: 27609403
- PMCID: PMC5329135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.09.004
The function of heparan sulfate during branching morphogenesis
Abstract
Branching morphogenesis is a fundamental process in the development of diverse epithelial organs such as the lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, prostate, salivary, lacrimal and mammary glands. A unifying theme during organogenesis is the importance of epithelial cell interactions with the extracellular matrix (ECM) and growth factors (GFs). The diverse developmental mechanisms giving rise to these epithelial organs involve many organ-specific GFs, but a unifying paradigm during organogenesis is the regulation of GF activity by heparan sulfates (HS) on the cell surface and in the ECM. This primarily involves the interactions of GFs with the sulfated side-chains of HS proteoglycans. HS is one of the most diverse biopolymers and modulates GF binding and signaling at the cell surface and in the ECM of all tissues. Here, we review what is known about how HS regulates branching morphogenesis of epithelial organs with emphasis on the developing salivary gland, which is a classic model to investigate epithelial-ECM interactions. We also address the structure, biosynthesis, turnover and function of HS during organogenesis. Understanding the regulatory mechanisms that control HS dynamics may aid in the development of therapeutic interventions for diseases and novel strategies for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Branching morphogenesis; Extracellular matrix; FGF10; FGFR2b; Growth factors; Heparan sulfate; Heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
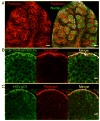
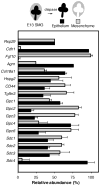
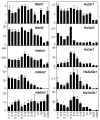
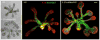
Similar articles
-
Dynamic Field Theory of Executive Function: Identifying Early Neurocognitive Markers.Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024 Dec;89(3):7-109. doi: 10.1111/mono.12478. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024. PMID: 39628288 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
"I've Spent My Whole Life Striving to Be Normal": Internalized Stigma and Perceived Impact of Diagnosis in Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):423-436. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0066. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116050 Free PMC article.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease mechanisms of monogenic congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022 Sep;190(3):325-343. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.32006. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 36208064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Matrisome, Inflammation, and Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2020 May;40(2):180-188. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3402516. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Semin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 31910448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary gland function, development, and regeneration.Physiol Rev. 2022 Jul 1;102(3):1495-1552. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2021. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35343828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRCA1 represses DNA replication initiation through antagonizing estrogen signaling and maintains genome stability in parallel with WEE1-MCM2 signaling during pregnancy.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Mar 1;28(5):842-857. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy398. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 30445628 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix modeling and remodeling: A biological interplay regulating tissue homeostasis and diseases.Matrix Biol. 2019 Jan;75-76:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30130584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

