Spt4 selectively regulates the expression of C9orf72 sense and antisense mutant transcripts
- PMID: 27516603
- PMCID: PMC5823025
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf7791
Spt4 selectively regulates the expression of C9orf72 sense and antisense mutant transcripts
Abstract
An expanded hexanucleotide repeat in C9orf72 causes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (c9FTD/ALS). Therapeutics are being developed to target RNAs containing the expanded repeat sequence (GGGGCC); however, this approach is complicated by the presence of antisense strand transcription of expanded GGCCCC repeats. We found that targeting the transcription elongation factor Spt4 selectively decreased production of both sense and antisense expanded transcripts, as well as their translated dipeptide repeat (DPR) products, and also mitigated degeneration in animal models. Knockdown of SUPT4H1, the human Spt4 ortholog, similarly decreased production of sense and antisense RNA foci, as well as DPR proteins, in patient cells. Therapeutic targeting of a single factor to eliminate c9FTD/ALS pathological features offers advantages over approaches that require targeting sense and antisense repeats separately.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
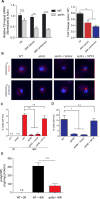
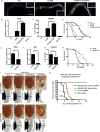
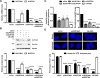
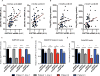
Comment in
-
NEURODEGENERATION. One target for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis therapy?Science. 2016 Aug 12;353(6300):647-8. doi: 10.1126/science.aah5408. Science. 2016. PMID: 27516584 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Suppression of the yeast elongation factor Spt4 ortholog reduces expanded SCA36 GGCCUG repeat aggregation and cytotoxicity.Brain Res. 2019 May 15;1711:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.12.045. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30610877
-
Transcription elongation factor AFF2/FMR2 regulates expression of expanded GGGGCC repeat-containing C9ORF72 allele in ALS/FTD.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 29;10(1):5466. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13477-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31784536 Free PMC article.
-
There has been an awakening: Emerging mechanisms of C9orf72 mutations in FTD/ALS.Brain Res. 2016 Sep 15;1647:19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27059391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic determinants and mechanisms of ALS/FTD linked to hexanucleotide repeat expansions in the C9orf72 gene.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jan 1;636:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 27619540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense transcripts of the expanded C9ORF72 hexanucleotide repeat form nuclear RNA foci and undergo repeat-associated non-ATG translation in c9FTD/ALS.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Dec;126(6):829-44. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1192-8. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 24129584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RNA-mediated toxicity in C9orf72 ALS and FTD.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Nov;145:105055. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105055. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32829028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of small molecule inhibitors to RNA polymerase-Spt5 complex impacts RNA and DNA stability.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2023 Nov 21;38(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10822-023-00543-z. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2023. PMID: 37987925 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Medicine for Frontotemporal Dementia.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Feb 21;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00075. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30846947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
eIF4B and eIF4H mediate GR production from expanded G4C2 in a Drosophila model for C9orf72-associated ALS.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Apr 25;7(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0711-9. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31023341 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting T7 RNA polymerase transcription in vitro with the Broccoli RNA aptamer as a simplified real-time fluorescent reporter.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100175. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014553. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33303627 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD021580/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS077402/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS094489/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS093865/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS079807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES20395/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS085812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097263/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS094489/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063964/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS063964/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS088689/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057553/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG026251/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS079725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS079807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS084528/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020395/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026251/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS077402/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS09386501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS085812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS084528/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS079725/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

