The ACE2 G8790A Polymorphism: Involvement in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Cerebral Stroke
- PMID: 27500554
- PMCID: PMC6817163
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22033
The ACE2 G8790A Polymorphism: Involvement in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Cerebral Stroke
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the correlations between ACE2 polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) combined with cerebral stroke (CS).
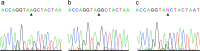
Methods: A total of 346 patients treated or hospitalized in our hospital were enrolled, including 181 cases without cerebrovascular complications (T2DM group) and 165 cases combined with CS (T2DM + CS group); 284 healthy individuals were selected as the control group. PCR-RFLP and ELISA were used to analyze ACE2 G8790A polymorphisms and serum ACE2 levels, respectively.
Results: Significant differences were observed in the genotype/allele frequency of ACE2 G8790A between the T2DM + CS and control groups, and the T2DM and T2DM + CS groups, and in the genotype frequency of ACE2 G8790A between the T2DM and the control groups. The A allele may increase the risk of T2DM combined with CS. The AA genotype may also increase the risk of T2DM combined with CS (OR = 3.733, 95%CI = 2.069-6.738; OR = 3.597, 95%CI = 1.884-6.867). Serum ACE2 levels showed statistically significant differences among the groups. Systolic pressure and diastolic pressure were protective factors of T2DM combined with CS.
Conclusion: The ACE2 G8790A polymorphism in T2DM patients was correlated with CS, and the A allele might be a risk factor of T2DM combined with CS.
Keywords: ACE2; allele frequency; cerebral stroke; gene polymorphism; regression analysis; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the relationship between ACE2 G8790A and AT2R A1675G gene polymorphisms in COVID-19 patients with and without lung involvement.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2024 Sep 20;18(4):157-170. doi: 10.2478/abm-2024-0022. eCollection 2024 Aug. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2024. PMID: 39309472 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene polymorphisms on type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Oct;17(19):2654-9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24142614
-
Investigation of angiotensin-1 converting enzyme 2 gene (G8790A) polymorphism in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy in Pakistani population.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 17;17(2):e0264038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264038. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35176079 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene polymorphisms and vulnerability to coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008 Aug;28(8):1365-8. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18753062 Chinese.
-
The MCP-1 Gene A-2518G Polymorphism Confers an Increased Risk of Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2015 Aug;19(8):411-7. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2014.0325. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2015. PMID: 26083329
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the relationship between ACE2 G8790A and AT2R A1675G gene polymorphisms in COVID-19 patients with and without lung involvement.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2024 Sep 20;18(4):157-170. doi: 10.2478/abm-2024-0022. eCollection 2024 Aug. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2024. PMID: 39309472 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms in clinical severity and outcomes of COVID-19 in Egypt.Afr J Lab Med. 2024 Aug 27;13(1):2375. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v13i1.2375. eCollection 2024. Afr J Lab Med. 2024. PMID: 39228902 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Genetic Variants in ACE1and ACE2 Genes with Susceptibility to COVID-19 Infection.Biochem Genet. 2024 Feb 13. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10722-8. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38349438
-
Combinatorial analysis of ACE and ACE2 polymorphisms reveals protection against COVID-19 worsening: A genetic association study in Brazilian patients.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 30;18(11):e0288178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288178. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38032879 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variants within SARS-CoV-2 Human Receptor Genes May Contribute to Variable Disease Outcomes in Different Ethnicities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 13;24(10):8711. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108711. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus – present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012;8:228–236. - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009;301:2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- Yang SH, Dou KF, Song WJ. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2425–2426; author reply 2426. - PubMed
-
- SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group , Liese AD, D'Agostino RB Jr, et al. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics 2006;118:1510–1518. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

