MicroRNA-21 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer, and tumor growth associated with down-regulation of sec23a expression
- PMID: 27495250
- PMCID: PMC4974737
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2628-z
MicroRNA-21 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer, and tumor growth associated with down-regulation of sec23a expression
Abstract
Background: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) is up-regulated in many cancers, including colorectal cancer (CRC). Nevertheless, the function of miR-21 in CRC and the mechanism underlying that function is still unclear.
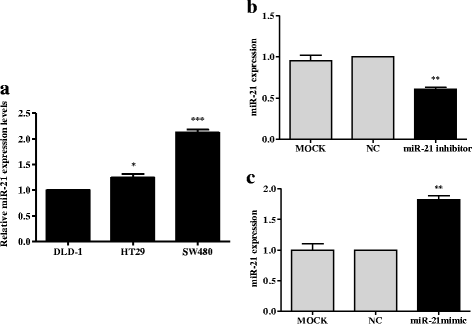
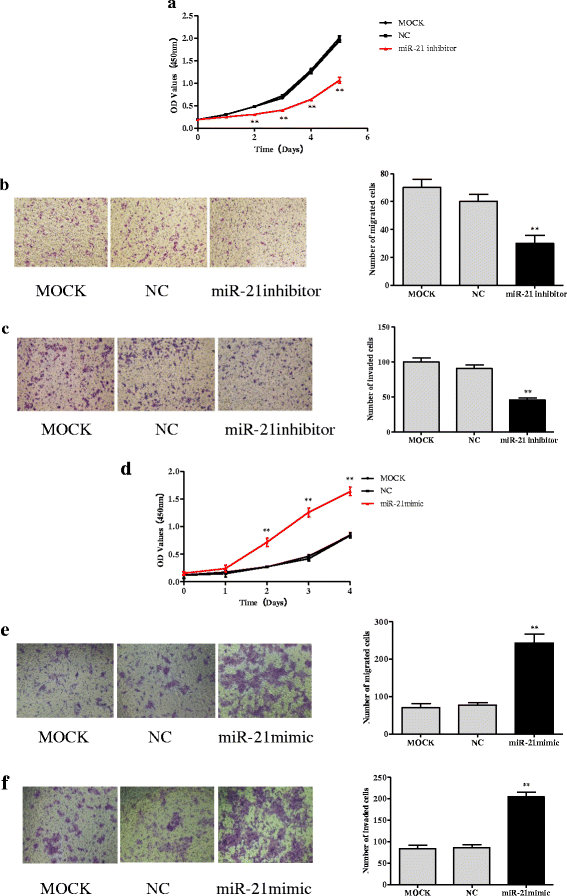
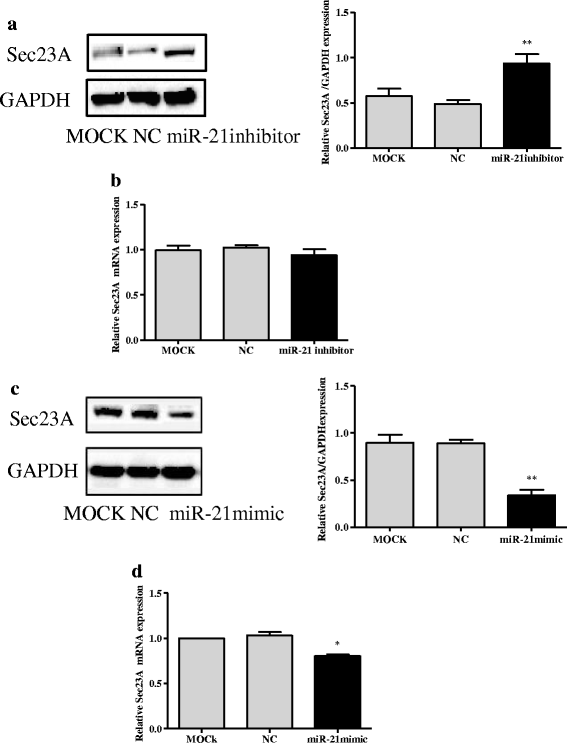
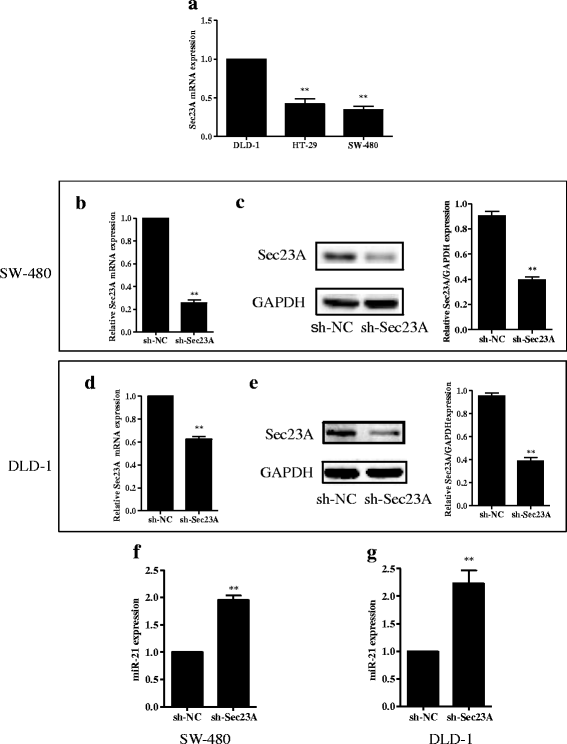
Methods: After analyzing the expression of miR-21 and Sec23A in CRC cell lines, we transfected the highest miR-21 expressing cell line, SW-480, with a plasmid containing an miR-21 inhibitor and the lowest miR-21 expressing cell line, DLD-1, with a plasmid containing an miR-21 mimic and measured the effects on the expression of Sec23A and on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. We also evaluated the effect of knocking down Sec23A on miR-21 expression and its effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Finally, we assessed the effect of miR-21 in a xenograft tumor model in mice. Tumor tissues from these mice were subjected to immunohistochemical staining to detect the expression of Sec23A.
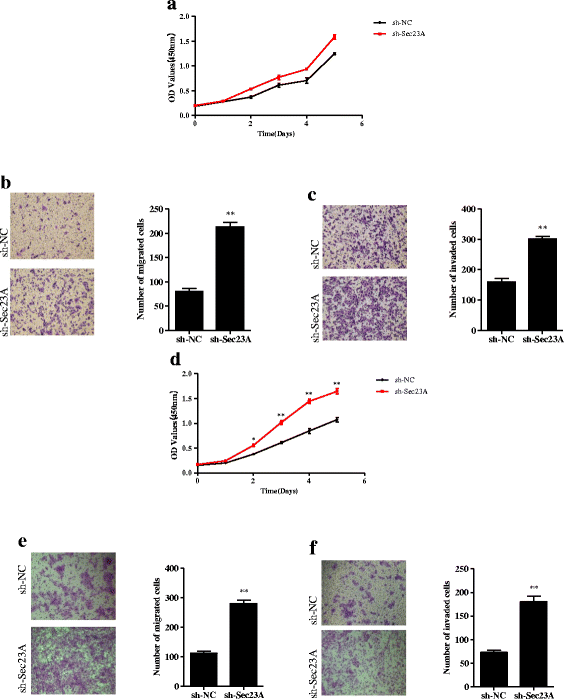
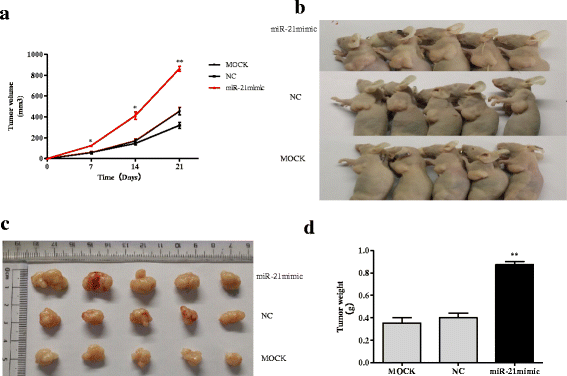
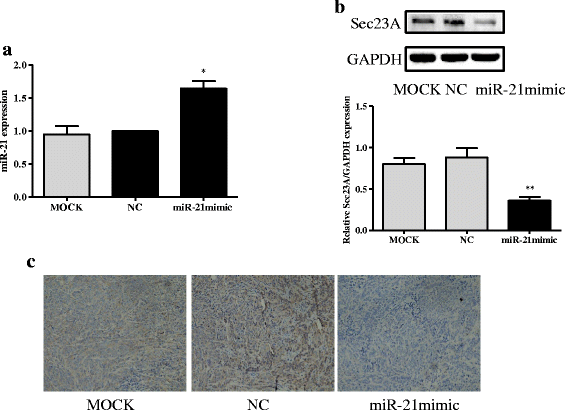
Results: Genetic deletion of miR-21 suppressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion of SW-480 cells, while over-expression of miR-21 promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of DLD-1 cells. Inhibition of miR-21 increased the expression of Sec23A protein in SW-480 cells while over-expression of miR-21 significantly suppressed the expression of Sec23A protein and Sec23A mRNA in DLD-1 cells. Knockdown of Sec23A increased the expression of miR-21 in SW480 and DLD-1 cells and their proliferation (DLD-1 only), migration, and invasion. Over-expression of miR-21 promoted tumor growth in BALB/c nude mice and suppressed tumor expression of Sec23A.
Conclusion: These findings provide novel insight into the molecular functions of miR-21 in CRC, which may serve as a potential interesting target.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Proliferation; Sec23A; Tumor growth; miR-21.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFα.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):145-156. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181503. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30010111
-
Genetic and epigenetic down-regulation of microRNA-212 promotes colorectal tumor metastasis via dysregulation of MnSOD.Gastroenterology. 2013 Aug;145(2):426-36.e1-6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23583431
-
microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):21380-21394. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28747. Epub 2019 May 17. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31102273
-
Mechanism and function of miR-140 in human cancers: A review and in silico study.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jan;241:154265. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154265. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36509008 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: microRNAs, miR-143 and -145, function as anti-oncomirs and the application of chemically modified miR-143 as an anti-cancer drug.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114(3):276-80. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10r12fm. Epub 2010 Oct 9. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20953119 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in microRNAs as Emerging Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 15;25(20):11060. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011060. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Functional Role of SEC23 in Vesicle Transportation, Autophagy and Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Sep 7;15(11):2419-2426. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.37008. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31595159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense Oligonucleotides against miR-21 Inhibit the Growth and Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma via the DUSP8 Pathway.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Dec 7;13:244-255. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 30317164 Free PMC article.
-
miR-21 antagonist alleviates colitis and angiogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in colitis mice induced by TNBS.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Apr;10(7):413. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-944. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35530951 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiling Predicts Nodal Status and Disease Recurrence in Patients Treated with Curative Intent for Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;14(9):2109. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092109. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vassiliki L, Tsikitis DWL, Marianne H, Lohse Patricia CM, Thompson A. Targeted therapy against chemoresistant colorectal cancers: Inhibition of p38alpha modulates the effect of cisplatin in vitro and in vivo through the tumor suppressor FoxO3A. Cancer Lett. 2014;344(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.10.035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

