Functional Consequences of Differential O-glycosylation of MUC1, MUC4, and MUC16 (Downstream Effects on Signaling)
- PMID: 27483328
- PMCID: PMC5039420
- DOI: 10.3390/biom6030034
Functional Consequences of Differential O-glycosylation of MUC1, MUC4, and MUC16 (Downstream Effects on Signaling)
Abstract
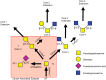
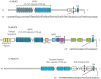
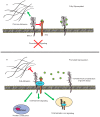
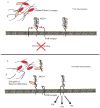
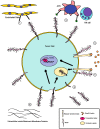
Glycosylation is one of the most abundant post-translational modifications that occur within the cell. Under normal physiological conditions, O-linked glycosylation of extracellular proteins is critical for both structure and function. During the progression of cancer, however, the expression of aberrant and truncated glycans is commonly observed. Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins that contain numerous sites of O-glycosylation within their extracellular domains. Transmembrane mucins also play a functional role in monitoring the surrounding microenvironment and transducing these signals into the cell. In cancer, these mucins often take on an oncogenic role and promote a number of pro-tumorigenic effects, including pro-survival, migratory, and invasive behaviors. Within this review, we highlight both the processes involved in the expression of aberrant glycan structures on mucins, as well as the potential downstream impacts on cellular signaling.
Keywords: MUC1; MUC16; MUC4; O-glycosylation; cancer; mucin; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of the transmembrane mucins, MUC1, MUC4 and MUC16, in normal endometrium and in endometriosis.Hum Reprod. 2014 Aug;29(8):1730-8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu146. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24939955 Free PMC article.
-
Mucins and Truncated O-Glycans Unveil Phenotypic Discrepancies between Serous Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines and Primary Tumours.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 13;19(7):2045. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072045. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011875 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of MUC4 in ovarian carcinoma: diagnostic significance alone and in combination with MUC1 and MUC16 (CA125).Mod Pathol. 2006 Oct;19(10):1386-94. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800646. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Mod Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16880776
-
The membrane-bound mucins: how large O-glycoproteins play key roles in epithelial cancers and hold promise as biological tools for gene-based and immunotherapies.Crit Rev Oncog. 2008;14(2-3):177-96. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v14.i2-3.30. Crit Rev Oncog. 2008. PMID: 19409062 Review.
-
Mucin Glycans: A Target for Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2023 Oct 11;28(20):7033. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207033. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The gut mucin-microbiota interactions: a missing key to optimizing endurance performance.Front Physiol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1284423. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1284423. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38074323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of cell-specific transcriptional responses in human colon tissue using CIBERSORTx.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 25;13(1):18281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45582-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37880448 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Changes in the Non-Inflamed Terminal Ileum of Patients with Ulcerative Colitis.Cells. 2020 Jul 28;9(8):1793. doi: 10.3390/cells9081793. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32731480 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Roles of O-Glycosylation.Molecules. 2018 Nov 23;23(12):3063. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123063. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30477085 Free PMC article.
-
α1,4-Linked N-acetylglucosamine suppresses gastric cancer development by inhibiting Mucin-1-mediated signaling.Cancer Sci. 2022 Nov;113(11):3852-3863. doi: 10.1111/cas.15530. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35959971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seregni E., Botti C., Massaron S., Lombardo C., Capobianco A., Bogni A., Bombardieri E. Structure, function and gene expression of epithelial mucins. Tumori. 1997;83:625–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

