Pancreatic cancer stem cell markers and exosomes - the incentive push
- PMID: 27468191
- PMCID: PMC4948278
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.5971
Pancreatic cancer stem cell markers and exosomes - the incentive push
Abstract
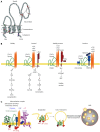
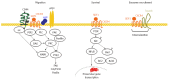
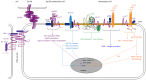
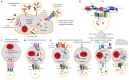
Pancreatic cancer (PaCa) has the highest death rate and incidence is increasing. Poor prognosis is due to late diagnosis and early metastatic spread, which is ascribed to a minor population of so called cancer stem cells (CSC) within the mass of the primary tumor. CSC are defined by biological features, which they share with adult stem cells like longevity, rare cell division, the capacity for self renewal, differentiation, drug resistance and the requirement for a niche. CSC can also be identified by sets of markers, which for pancreatic CSC (Pa-CSC) include CD44v6, c-Met, Tspan8, alpha6beta4, CXCR4, CD133, EpCAM and claudin7. The functional relevance of CSC markers is still disputed. We hypothesize that Pa-CSC markers play a decisive role in tumor progression. This is fostered by the location in glycolipid-enriched membrane domains, which function as signaling platform and support connectivity of the individual Pa-CSC markers. Outside-in signaling supports apoptosis resistance, stem cell gene expression and tumor suppressor gene repression as well as miRNA transcription and silencing. Pa-CSC markers also contribute to motility and invasiveness. By ligand binding host cells are triggered towards creating a milieu supporting Pa-CSC maintenance. Furthermore, CSC markers contribute to the generation, loading and delivery of exosomes, whereby CSC gain the capacity for a cell-cell contact independent crosstalk with the host and neighboring non-CSC. This allows Pa-CSC exosomes (TEX) to reprogram neighboring non-CSC towards epithelial mesenchymal transition and to stimulate host cells towards preparing a niche for metastasizing tumor cells. Finally, TEX communicate with the matrix to support tumor cell motility, invasion and homing. We will discuss the possibility that CSC markers are the initial trigger for these processes and what is the special contribution of CSC-TEX.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Crosstalk; Exosomes; Pancreatic cancer; Stem cell markers.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pancreatic cancer-initiating cell exosome message transfer into noncancer-initiating cells: the importance of CD44v6 in reprogramming.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 19;38(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1129-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30890157 Free PMC article.
-
The tetraspanins CD151 and Tspan8 are essential exosome components for the crosstalk between cancer initiating cells and their surrounding.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 10;6(4):2366-84. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2958. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25544774 Free PMC article.
-
CD44v6-competent tumor exosomes promote motility, invasion and cancer-initiating cell marker expression in pancreatic and colorectal cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 23;7(34):55409-55436. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10580. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27419629 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes, metastases, and the miracle of cancer stem cell markers.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019 Jun;38(1-2):259-295. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09793-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019. PMID: 31030373 Review.
-
Never let it go: Stopping key mechanisms underlying metastasis to fight pancreatic cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2017 Jun;44:43-59. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017. PMID: 28438662 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles from Echinococcus granulosus larval stage: Isolation, characterization and uptake by dendritic cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jan 7;13(1):e0007032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007032. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30615613 Free PMC article.
-
Updated therapeutic outcome for patients with periampullary and pancreatic cancer related to recent translational research.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec 28;22(48):10502-10511. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10502. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 28082802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pancreatic Cancer-Initiating Cell Marker CD44v6 Affects Transcription, Translation, and Signaling: Consequences for Exosome Composition and Delivery.J Oncol. 2019 Aug 7;2019:3516973. doi: 10.1155/2019/3516973. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31485223 Free PMC article.
-
Profound Reprogramming towards Stemness in Pancreatic Cancer Cells as Adaptation to AKT Inhibition.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 5;12(8):2181. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082181. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32764385 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cells are Actually Stem Cells with Disordered Differentiation: the Monophyletic Origin of Cancer.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 May;19(4):827-838. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10508-2. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36648606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Lai ST, Xie L, Zhao JD, Ma NY, Zhu J, Ren ZG, Jiang GL. Metformin is associated with reduced risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;106:19–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

