Multiple Transcripts Encode Full-Length Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 and IE2 Proteins during Lytic Infection
- PMID: 27466417
- PMCID: PMC5021424
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00741-16
Multiple Transcripts Encode Full-Length Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 and IE2 Proteins during Lytic Infection
Abstract
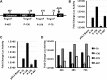
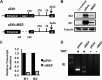
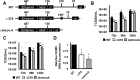
Expression of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) IE1 and IE2 proteins is critical for the establishment of lytic infection and reactivation from viral latency. Defining the mechanisms controlling IE1 and IE2 expression is therefore important for understanding how HCMV regulates its replicative cycle. Here we identify several novel transcripts encoding full-length IE1 and IE2 proteins during HCMV lytic replication. Two of the alternative major immediate early (MIE) transcripts initiate in the first intron, intron A, of the previously defined MIE transcript, while others extend the 5' untranslated region. Each of the MIE transcripts associates with polyribosomes in infected cells and therefore contributes to IE1 and IE2 protein levels. Surprisingly, deletion of the core promoter region of the major immediate early promoter (MIEP) from a plasmid containing the MIE genomic locus did not completely abrogate IE1 and IE2 expression. Instead, deletion of the MIEP core promoter resulted in increased expression of alternative MIE transcripts, suggesting that the MIEP suppresses the activity of the alternative MIE promoters. While the canonical MIE mRNA was the most abundant transcript at immediate early times, the novel MIE transcripts accumulated to levels equivalent to that of the known MIE transcript later in infection. Using two HCMV recombinants, we found that sequences in intron A of the previously defined MIE transcript are required for efficient IE1 and IE2 expression and viral replication. Together, our results identify new regulatory sequences controlling IE1 and IE2 expression and suggest that multiple transcription units act in concert to regulate IE1 and IE2 expression during lytic infection.
Importance: The HCMV IE1 and IE2 proteins are critical regulators of HCMV replication, both during primary infection and reactivation from viral latency. This study expands our understanding of the sequences controlling IE1 and IE2 expression by defining novel transcriptional units controlling the expression of full-length IE1 and IE2 proteins. Our results suggest that alternative promoters may allow for IE1 and IE2 expression when MIEP activity is limiting, as occurs in latently infected cells.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


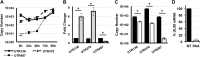
Similar articles
-
Specific RNA structures in the 5' untranslated region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early transcript are critical for efficient virus replication.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0262123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02621-23. Epub 2024 Jan 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38165154 Free PMC article.
-
The 5' Untranslated Region of the Major Immediate Early mRNA Is Necessary for Efficient Human Cytomegalovirus Replication.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e02128-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02128-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29343581 Free PMC article.
-
Two Polypyrimidine Tracts in Intron 4 of the Major Immediate Early Gene Are Critical for Gene Expression Switching from IE1 to IE2 and for Replication of Human Cytomegalovirus.J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7339-7349. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00837-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27252533 Free PMC article.
-
Bright and Early: Inhibiting Human Cytomegalovirus by Targeting Major Immediate-Early Gene Expression or Protein Function.Viruses. 2020 Jan 16;12(1):110. doi: 10.3390/v12010110. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31963209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus latency is associated with the state of differentiation of the host cells: an in vitro model in teratocarcinoma cells.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005;52(3-4):397-406. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.52.2005.3-4.11. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005. PMID: 16400879 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific RNA structures in the 5' untranslated region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate early transcript are critical for efficient virus replication.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0262123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02621-23. Epub 2024 Jan 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38165154 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus decathlon: Ten critical replication events provide opportunities for restriction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 25;10:1053139. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1053139. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision mouse models with expanded tropism for human pathogens.Nat Biotechnol. 2019 Oct;37(10):1163-1173. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0225-9. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Nat Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31451733 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and host network analysis of the human cytomegalovirus transcriptome in latency.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 21:2024.05.21.594597. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.21.594597. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38826434 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Control of Immediate Early Gene Expression for Human Cytomegalovirus Reactivation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 17;10:476. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00476. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33072616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

