Metabolic Profiling of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Comparison with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome and Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 27441838
- PMCID: PMC4956266
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159384
Metabolic Profiling of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Comparison with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome and Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
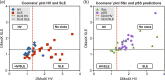
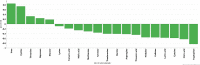
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease which can affect most organ systems including skin, joints and the kidney. Clinically, SLE is a heterogeneous disease and shares features of several other rheumatic diseases, in particular primary Sjögrens syndrome (pSS) and systemic sclerosis (SSc), why it is difficult to diagnose The pathogenesis of SLE is not completely understood, partly due to the heterogeneity of the disease. This study demonstrates that metabolomics can be used as a tool for improved diagnosis of SLE compared to other similar autoimmune diseases. We observed differences in metabolic profiles with a classification specificity above 67% in the comparison of SLE with pSS, SSc and a matched group of healthy individuals. Selected metabolites were also significantly different between studied diseases. Biochemical pathway analysis was conducted to gain understanding of underlying pathways involved in the SLE pathogenesis. We found an increased oxidative activity in SLE, supported by increased xanthine oxidase activity and an increased turnover in the urea cycle. The most discriminatory metabolite observed was tryptophan, with decreased levels in SLE patients compared to control groups. Changes of tryptophan levels were related to changes in the activity of the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) and/or to activation of the kynurenine pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Connective tissue diseases: Promises and challenges of metabolomics in SLE.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;12(11):627-628. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.163. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27708401 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
TBK1: A key regulator and potential treatment target for interferon positive Sjögren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis.J Autoimmun. 2018 Jul;91:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 29673738
-
Shared gut, but distinct oral microbiota composition in primary Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus.J Autoimmun. 2019 Feb;97:77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 30416033
-
Excess Productivity Costs of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic Sclerosis, and Sjögren's Syndrome: A General Population-Based Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019 Jan;71(1):142-154. doi: 10.1002/acr.23573. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 29648677
-
Apoptosis in rheumatic diseases.Am J Med. 2000 Jan;108(1):73-82. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00332-0. Am J Med. 2000. PMID: 11059443 Review. No abstract available.
-
Connective tissue disorders: systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren's syndrome, and scleroderma.Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;119:463-73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-7020-4086-3.00030-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24365313 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Alterations in Systemic Sclerosis.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 21;8:761721. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.761721. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34993231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fecal Metabolomics and Potential Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2019 May 3;10:976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00976. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31130958 Free PMC article.
-
A Case Report of Switching from Specific Vendor-Based to R-Based Pipelines for Untargeted LC-MS Metabolomics.Metabolites. 2020 Jan 8;10(1):28. doi: 10.3390/metabo10010028. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 31936230 Free PMC article.
-
Rab4A-directed endosome traffic shapes pro-inflammatory mitochondrial metabolism in T cells via mitophagy, CD98 expression, and kynurenine-sensitive mTOR activation.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 22;15(1):2598. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46441-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38519468 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of Avocado Oil Adulteration Using Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance.Foods. 2022 Apr 14;11(8):1134. doi: 10.3390/foods11081134. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35454721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stahl-Hallengren C, Jonsen A, Nive O, Sturfelt G. Incidence studies of systemic lupus erythematosus in Southern Sweden: increasing age, decreasing frequency of renal manifestations and good prognosis. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27(3): 685–691. - PubMed
-
- Fries J. F, Holman, H. R. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a clinical analysis. Major Probl Intern Med. 1975; 6: v–199. - PubMed
-
- Sturfelt G, Sjöholm AG. Complement components, complement activation, and acute phase response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984; 75: 75–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

