Structural basis of Smoothened regulation by its extracellular domains
- PMID: 27437577
- PMCID: PMC4970916
- DOI: 10.1038/nature18934
Structural basis of Smoothened regulation by its extracellular domains
Abstract
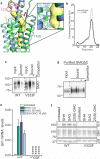
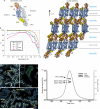
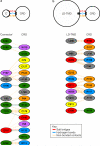
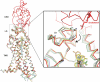
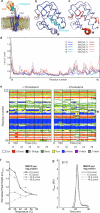
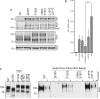
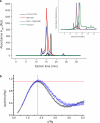
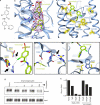
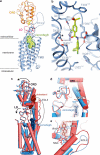
Developmental signals of the Hedgehog (Hh) and Wnt families are transduced across the membrane by Frizzledclass G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) composed of both a heptahelical transmembrane domain (TMD) and an extracellular cysteine-rich domain (CRD). How the large extracellular domains of GPCRs regulate signalling by the TMD is unknown. We present crystal structures of the Hh signal transducer and oncoprotein Smoothened, a GPCR that contains two distinct ligand-binding sites: one in its TMD and one in the CRD. The CRD is stacked a top the TMD, separated by an intervening wedge-like linker domain. Structure-guided mutations show that the interface between the CRD, linker domain and TMD stabilizes the inactive state of Smoothened. Unexpectedly, we find a cholesterol molecule bound to Smoothened in the CRD binding site. Mutations predicted to prevent cholesterol binding impair the ability of Smoothened to transmit native Hh signals. Binding of a clinically used antagonist, vismodegib, to the TMD induces a conformational change that is propagated to the CRD, resulting in loss of cholesterol from the CRD-linker domain-TMD interface. Our results clarify the structural mechanism by which the activity of a GPCR is controlled by ligand-regulated interactions between its extracellular and transmembrane domains.
Figures

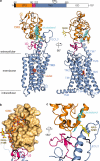
Similar articles
-
Structure and function of the Smoothened extracellular domain in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling.Elife. 2013 Oct 29;2:e01340. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01340. Elife. 2013. PMID: 24171105 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the role of the Smoothened cysteine-rich domain in Hedgehog signalling.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2965. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3965. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24351982 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of Smoothened Activation in Hedgehog Signaling.Cell. 2018 Jul 12;174(2):312-324.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.029. Epub 2018 May 24. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29804838 Free PMC article.
-
[Structure of the Smoothened receptor].Med Sci (Paris). 2013 Oct;29(10):855-60. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20132910012. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Med Sci (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24148123 Review. French.
-
Smoothened goes molecular: new pieces in the hedgehog signaling puzzle.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3500-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.617936. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25519909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological targeting of smoothened receptor cysteine-rich domain by Budesonide promotes in vitro myelination.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Oct 15;17:1473960. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1473960. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39473481 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and more: FDA-approved novel therapeutic drugs for solid tumors from 1991 to 2021.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Oct 8;15(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01362-9. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36209184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sterol regulation of developmental and oncogenic Hedgehog signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;196:114647. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114647. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34111427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Synthesis of New Withaferin A Inspired Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors.Chemistry. 2021 Jun 4;27(32):8350-8357. doi: 10.1002/chem.202100315. Epub 2021 May 4. Chemistry. 2021. PMID: 33811701 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol activates the G-protein coupled receptor Smoothened to promote Hedgehog signaling.Elife. 2016 Oct 5;5:e20304. doi: 10.7554/eLife.20304. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27705744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharpe HJ, Wang W, Hannoush RN, de Sauvage FJ. Regulation of the oncoprotein Smoothened by small molecules. Nature chemical biology. 2015;11:246–255. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1776. - PubMed
-
- Taipale J, et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in Smoothened and Patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature. 2000;406:1005–1009. doi:10.1038/35023008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 102890/Z/13/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R35 GM118082/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM106078/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 14414/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C20724/A14414/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 092970/Z/10/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 GM106078/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007276/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL067773/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL067773/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

