Sar1 localizes at the rims of COPII-coated membranes in vivo
- PMID: 27432890
- PMCID: PMC5047700
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.189423
Sar1 localizes at the rims of COPII-coated membranes in vivo
Abstract
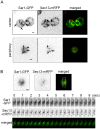
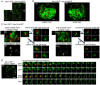
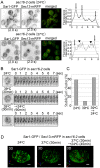
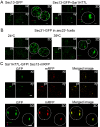
The Sar1 GTPase controls coat assembly on coat protein complex II (COPII)-coated vesicles, which mediate protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi. The GTP-bound form of Sar1, activated by the ER-localized guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Sec12, associates with the ER membrane. GTP hydrolysis by Sar1, stimulated by the COPII-vesicle-localized GTPase-activating protein (GAP) Sec23, in turn causes Sar1 to dissociate from the membrane. Thus, Sar1 is cycled between active and inactive states, and on and off vesicle membranes, but its precise spatiotemporal regulation remains unknown. Here, we examined Sar1 localization on COPII-coated membranes in living Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Two-dimensional (2D) observation demonstrated that Sar1 showed modest accumulation around the ER exit sites (ERES) in a manner that was dependent on Sec16 function. Detailed three-dimensional (3D) observation further demonstrated that Sar1 localized at the rims of the COPII-coated membranes, but was excluded from the rest of the COPII membranes. Additionally, a GTP-locked form of Sar1 induced abnormally enlarged COPII-coated structures and covered the entirety of these structures. These results suggested that the reversible membrane association of Sar1 GTPase leads to its localization being restricted to the rims of COPII-coated membranes in vivo.
Keywords: COPII-coated vesicle; ER; GTP hydrolysis; Sar1; Sec16.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into structural and regulatory roles of Sec16 in COPII vesicle formation at ER exit sites.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Aug;23(15):2930-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0356. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22675024 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Sar1 NH2 terminus by GTP binding and hydrolysis promotes membrane deformation to control COPII vesicle fission.J Cell Biol. 2005 Dec 19;171(6):919-24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200509095. Epub 2005 Dec 12. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16344311 Free PMC article.
-
Sed4p stimulates Sar1p GTP hydrolysis and promotes limited coat disassembly.Traffic. 2011 May;12(5):591-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01173.x. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21291503
-
The small GTPase Sar1, control centre of COPII trafficking.FEBS Lett. 2023 Mar;597(6):865-882. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14595. Epub 2023 Feb 20. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36737236 Review.
-
COPII coat assembly and selective export from the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biochem. 2004 Dec;136(6):755-60. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh184. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15671485 Review.
Cited by
-
The Golgi Apparatus and its Next-Door Neighbors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 28;10:884360. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.884360. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coat flexibility in the secretory pathway: a role in transport of bulky cargoes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019 Aug;59:104-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 May 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31125831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COPII-mediated trafficking at the ER/ERGIC interface.Traffic. 2019 Jul;20(7):491-503. doi: 10.1111/tra.12654. Epub 2019 May 30. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31059169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ER-Golgi Transport Dynamics by GTPases in Budding Yeast.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Jan 24;5:122. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00122. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29473037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TANGO1 recruits Sec16 to coordinately organize ER exit sites for efficient secretion.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 5;216(6):1731-1743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201703084. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28442536 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

