The type I interferon signature in leukocyte subsets from peripheral blood of patients with early arthritis: a major contribution by granulocytes
- PMID: 27411379
- PMCID: PMC4944477
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1065-3
The type I interferon signature in leukocyte subsets from peripheral blood of patients with early arthritis: a major contribution by granulocytes
Abstract
Background: The type I interferon (IFN) signature in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has shown clinical relevance in relation to disease onset and therapeutic response. Identification of the cell type(s) contributing to this IFN signature could provide insight into the signature's functional consequences. The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of peripheral leukocyte subsets to the IFN signature in early arthritis.
Methods: Blood was collected from 26 patients with early arthritis and lysed directly or separated into peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMNs). PBMCs were sorted into CD4(+) T cells, CD8(+) T cells, CD19(+) B cells, and CD14(+) monocytes by flow cytometry. Messenger RNA expression of three interferon response genes (IRGs RSAD2, IFI44L, and MX1) and type I interferon receptors (IFNAR1 and IFNAR2) was determined in whole blood and blood cell subsets by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. IRG expression was averaged to calculate an IFN score for each sample.
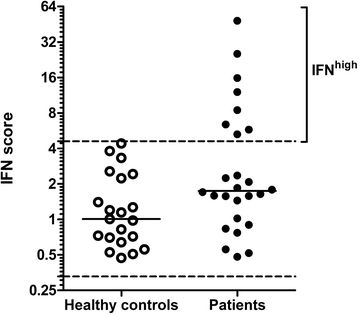
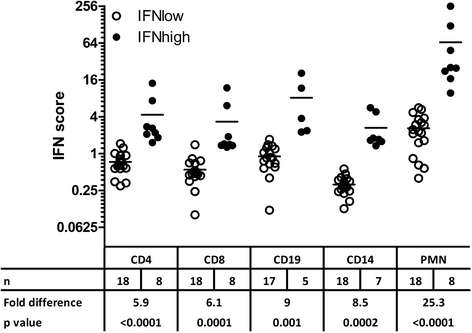
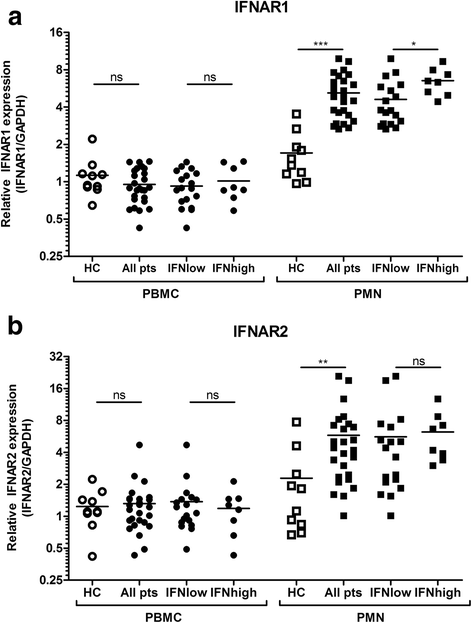
Results: Patients were designated "IFN(high)" (n = 8) or "IFN(low)" (n = 18) on the basis of an IFN score cutoff in whole peripheral blood from healthy control subjects. The difference in IFN score between IFN(high) and IFN(low) patients was remarkably large for the PMN fraction (mean 25-fold) compared with the other subsets (mean 6- to 9-fold), indicating that PMNs are the main inducers of IRGs. Moreover, the relative contribution of the PMN fraction to the whole-blood IFN score was threefold higher than expected from its abundance in blood (p = 0.008), whereas it was three- to sixfold lower for the other subsets (p ≤ 0.063), implying that the PMNs are most sensitive to IFN signaling. Concordantly, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 were upregulated compared with healthy controls selectively in patient PMNs (p ≤ 0.0077) but not in PBMCs.
Conclusions: PMNs are the main contributors to the whole-blood type I IFN signature in patients with early arthritis, which seems due to increased sensitivity of these cells to type I IFN signaling. Considering the well-established role of neutrophils in the pathology of arthritis, this suggests a role of type I IFN activity in the disease as well.
Keywords: Granulocytes; Rheumatoid arthritis; Type I interferon.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IRF4 and IRGs Delineate Clinically Relevant Gene Expression Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 7;9:3085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03085. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30666255 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IFN-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024 Feb;26(2):37-52. doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01125-6. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38051494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon response gene expression in established rheumatoid arthritis is not associated with clinical parameters.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Dec 12;18(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1191-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27955694 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma production in response to in vitro stimulation with collagen type II in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with HLA-DRB1(*)0401 and HLA-DQ8.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):75-84. doi: 10.1186/ar71. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219392 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of peripheral blood from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review.Inflamm Regen. 2018 Nov 5;38:21. doi: 10.1186/s41232-018-0078-5. eCollection 2018. Inflamm Regen. 2018. PMID: 30410636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential CpG DNA methylation in peripheral naïve CD4+ T-cells in early rheumatoid arthritis patients.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 Apr 7;12(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-00837-1. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32264938 Free PMC article.
-
IRF4 and IRGs Delineate Clinically Relevant Gene Expression Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 7;9:3085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03085. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30666255 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological effects of everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;30(4):341-352. doi: 10.1177/0394632017734459. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28988508 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis-relevant DNA methylation changes identified in ACPA-positive asymptomatic individuals using methylome capture sequencing.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jul 31;11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0699-9. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31366403 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IFN-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024 Feb;26(2):37-52. doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01125-6. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38051494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van der Pouw Kraan TC, Wijbrandts CA, van Baarsen LG, Voskuyl AE, Rustenburg F, Baggen JM, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis subtypes identified by genomic profiling of peripheral blood cells: assignment of a type I interferon signature in a subpopulation of patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1008–14. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.063412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantaert T, van Baarsen LG, Wijbrandts CA, Thurlings RM, van de Sande MG, Bos C, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Verweij CL, Tak PP, Baeten DL. Type I interferons have no major influence on humoral autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:156–66. - PubMed
-
- van Baarsen LG, Bos WH, Rustenburg F, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Wolbink GJ, Dijkmans BA, van SD, Verweij CL. Gene expression profiling in autoantibody-positive patients with arthralgia predicts development of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:694–704. - PubMed
-
- Lübbers J, Brink M, van de Stadt LA, Vosslamber S, Wesseling JG, van Schaardenburg D, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Verweij CL. The type I IFN signature as a biomarker of preclinical rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:776–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

