MET Inhibition in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 27390595
- PMCID: PMC4934028
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.14604
MET Inhibition in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most lethal form of kidney cancer. Small molecule VEGFR inhibitors are widely used but are not curative and various resistance mechanisms such as activation of the MET pathway have been described. Dual MET/VEGFR2 inhibitors have recently shown clinical benefit but limited preclinical data evaluates their effects in ccRCC.
Methods: An interrogation of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset was performed to evaluate oncogenic alterations in the MET/VEGFR2 pathway. We evaluated the in vitro effects of Cabozantinib, a dual MET/VEGFR2 inhibitor, using a panel of ccRCC cell lines. Drug effects of cell viability and proliferation, migration, cell scatter, anchorage independent growth, and downstream MET/VEGFR2 signaling pathways were assessed.
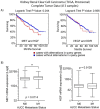
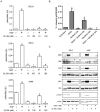
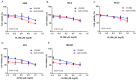
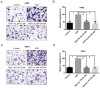
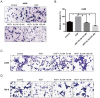
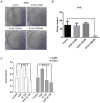
Results: Twelve percent of TCGA cases had possible MET/HGF oncogenic alterations with co-occurrence noted (p<0.001). MET/HGF altered cases had worse overall survival (p=0.044). Cabozantinib was a potent inhibitor of MET and VEGFR2 in vitro in our cell line panel. PI3K, MAPK and mTOR pathways were also suppressed by cabozantinib, however the effects on cell viability in vitro were modest. At nanomolar concentrations of cabozantinib, HGF-stimulated migration, invasion, cellular scattering and soft agar colony formation were inhibited.
Conclusions: We provide further preclinical rationale for dual MET/VEGFR2 inhibition in ccRCC. While the MET pathway is implicated in VEGFR resistance, dual inhibitors may have direct anti-tumor effects in a patient subset with evidence of MET pathway involvement. Cabozantinib is a potent dual MET/VEGFR2 inhibitor, significantly inhibits cell migration and invasion in vitro and likely has anti-angiogenic effects similar to other VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Future work involving in vivo models will be useful to better define mechanisms of potential anti-tumor activity.
Keywords: HGF; MET; VEGFR2; XL184; cabozantinib.; clear cell Carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors report no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition using cabozantinib overcomes HGF/MET signaling mediated resistance to pan-VEGFR inhibition in orthotopic and metastatic neuroblastoma tumors.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):203-211. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3792. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27922668
-
Cabozantinib suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by a dual blockade of VEGFR2 and MET.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 1;20(11):2959-70. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2620. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24700742
-
Dual blockade of MET and VEGFR2 signaling pathways as a potential therapeutic maneuver for peritoneal carcinomatosis in scirrhous gastric cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Apr 16;600:80-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.045. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35196631
-
Cabozantinib: Multi-kinase Inhibitor of MET, AXL, RET, and VEGFR2.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018;211:67-75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91442-8_5. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30069760 Review.
-
Cabozantinib: a MET, RET, and VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;201:207-14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54490-3_12. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24756794 Review.
Cited by
-
Long Non-coding RNA CCAT1 Acts as an Oncogene and Promotes Sunitinib Resistance in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 25;10:516552. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.516552. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33072561 Free PMC article.
-
New Therapeutic Interventions for Kidney Carcinoma: Looking to the Future.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;14(15):3616. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153616. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cabozantinib and dasatinib synergize to induce tumor regression in non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Rep Med. 2021 May 7;2(5):100267. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100267. eCollection 2021 May 18. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34095877 Free PMC article.
-
Cabozantinib as first-line treatment in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a profile of its use.Drugs Ther Perspect. 2018;34(10):457-465. doi: 10.1007/s40267-018-0547-6. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Drugs Ther Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30679901 Free PMC article.
-
MET exon 14 juxtamembrane splicing mutations: clinical and therapeutical perspectives for cancer therapy.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Jan;5(1):2. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.12.33. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28164087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- (NCCN) NCCN. Kidney Cancer. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology; 2012.
-
- Rini BI. Vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma: current status and future directions. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2007;13:1098–106. - PubMed
-
- Shojaei F, Lee JH, Simmons BH, Wong A, Esparza CO, Plumlee PA. et al. HGF/c-Met acts as an alternative angiogenic pathway in sunitinib-resistant tumors. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10090–100. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt L, Duh FM, Chen F, Kishida T, Glenn G, Choyke P. et al. Germline and somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the MET proto-oncogene in papillary renal carcinomas. Nature genetics. 1997;16:68–73. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

