Dual and Specific Inhibition of NAMPT and PAK4 By KPT-9274 Decreases Kidney Cancer Growth
- PMID: 27390344
- PMCID: PMC5010932
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0197
Dual and Specific Inhibition of NAMPT and PAK4 By KPT-9274 Decreases Kidney Cancer Growth
Abstract
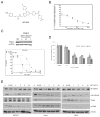
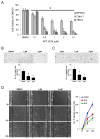
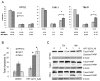
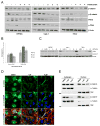
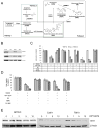
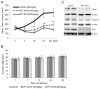
Kidney cancer (or renal cell carcinoma, RCC) is the sixth most common malignancy in the United States and one of the relatively few whose incidence is increasing. Because of the near universal resistance which occurs with the use of current treatment regimens, reprogrammed metabolic pathways are being investigated as potential targets for novel therapies of this disease. Borrowing from studies on other malignancies, we have identified the PAK4 and NAD biosynthetic pathways as being essential for RCC growth. We now show, using the dual PAK4/NAMPT inhibitor KPT-9274, that interference with these signaling pathways results in reduction of G2-M transit as well as induction of apoptosis and decrease in cell invasion and migration in several human RCC cell lines. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that inhibition of the PAK4 pathway by KPT-9274 attenuates nuclear β-catenin as well as the Wnt/β-catenin targets cyclin D1 and c-Myc. Furthermore, NAPRT1 downregulation, which we show occurs in all RCC cell lines tested, makes this tumor highly dependent on NAMPT for its NAD requirements, such that inhibition of NAMPT by KPT-9274 leads to decreased survival of these rapidly proliferating cells. When KPT-9274 was administered in vivo to a 786-O (VHL-mut) human RCC xenograft model, there was dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth with no apparent toxicity; KPT-9274 demonstrated the expected on-target effects in this mouse model. KPT-9274 is being evaluated in a phase I human clinical trial in solid tumors and lymphomas, which will allow this data to be rapidly translated into the clinic for the treatment of RCC. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(9); 2119-29. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
W.S., E.B., and C.A. are employees of Karyopharm and made suggestions on the manuscript but did not influence the direction of the research reported here. Some of the reagents in this study were ordered by Karyopharm and gifted to the Weiss laboratory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KPT-9274, an Inhibitor of PAK4 and NAMPT, Leads to Downregulation of mTORC2 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2020 Feb 17;33(2):482-491. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00376. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31876149 Free PMC article.
-
Dual PAK4-NAMPT Inhibition Impacts Growth and Survival, and Increases Sensitivity to DNA-Damaging Agents in Waldenström Macroglobulinemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 1;25(1):369-377. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1776. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30206161 Free PMC article.
-
Anticystogenic activity of a small molecule PAK4 inhibitor may be a novel treatment for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Kidney Int. 2017 Oct;92(4):922-933. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 May 23. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28545714 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the vulnerability to NAD+ depletion in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leukemia. 2018 Mar;32(3):616-625. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.281. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Leukemia. 2018. PMID: 28904384
-
Inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) as a therapeutic strategy in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jul;151:16-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25709099 Review.
Cited by
-
P-21 Activated Kinases in Liver Disorders.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 16;15(2):551. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020551. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Rate-Limiting Enzyme to Therapeutic Target: The Promise of NAMPT in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 12;13:920113. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.920113. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35903330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Ones to Fight a Big Problem-Intervention of Cancer Metastasis by Small Molecules.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 3;12(6):1454. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061454. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32503267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TBC1D10B promotes tumor progression in colon cancer via PAK4‑mediated promotion of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Apoptosis. 2024 Aug;29(7-8):1185-1197. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01972-3. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38824479
-
Role of NAD+ and mitochondrial sirtuins in cardiac and renal diseases.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Apr;13(4):213-225. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.5. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28163307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

