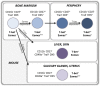
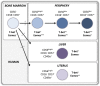
T-bet and Eomesodermin in NK Cell Development, Maturation, and Function
- PMID: 27379101
- PMCID: PMC4913100
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00241
T-bet and Eomesodermin in NK Cell Development, Maturation, and Function
Abstract
Recent reports give insights into the role of the T-box transcription factors, T-bet and Eomesodermin (Eomes), in NK cell biology. In this mini-review, we recapitulate the initial reports that delineate T-bet and Eomes as master regulators of NK cell development, maturation, and function. We discuss how T-bet and Eomes expression is regulated during NK cell development and peripheral maturation. Furthermore, we summarize the current literature on the role of T-bet and Eomes in the transcriptional regulation of NK cell function and review possible effects of T-box transcription factor anomalies during aging, infection, cancer, and after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. We discuss how the current data argue in favor of a model of T-bet and Eomes synergy in transcriptional regulation of NK cell function and identify T-box transcription factors as potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Eomes; T-bet; T-box transcription factors; natural killer cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-BET and EOMES Accelerate and Enhance Functional Differentiation of Human Natural Killer Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 24;12:732511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732511. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34630413 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of T-bet and Eomes during Maturation of Peripheral Blood NK Cells Does Not Depend on Licensing/Educating KIR.Front Immunol. 2016 Aug 24;7:299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00299. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27605928 Free PMC article.
-
Differential transcription of Eomes and T-bet during maturation of mouse uterine natural killer cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Dec;78(6):1347-55. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0305142. Epub 2005 Oct 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16204645
-
T-bet and Eomes govern differentiation and function of mouse and human NK cells and ILC1.Eur J Immunol. 2018 May;48(5):738-750. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747299. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29424438 Review.
-
Regulatory roles of transcription factors T-bet and Eomes in group 1 ILCs.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 1):113229. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113229. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39357208 Review.
Cited by
-
T-BET and EOMES Accelerate and Enhance Functional Differentiation of Human Natural Killer Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 24;12:732511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732511. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34630413 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Ascaris infection impairs the effector functions of natural killer cells in single and Salmonella co-infected pigs.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 25;14(1):14586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64497-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38918457 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 13;9:1869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01869. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30150991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Innate Immune Cell-Tumor Microenvironment Crosstalk at a Single-Cell Level.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 13;10:803947. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.803947. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Cues Direct Skin-Resident Type 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells to Adopt a Psoriasis-Promoting Identity.JID Innov. 2023 Apr 25;3(4):100204. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2023.100204. eCollection 2023 Jul. JID Innov. 2023. PMID: 37533580 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources