High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22
- PMID: 27350069
- PMCID: PMC4924095
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28990
High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22
Abstract
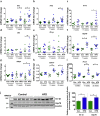
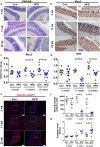
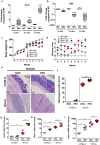
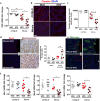
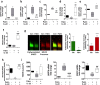
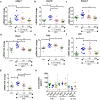
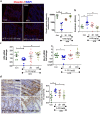
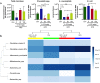
Prolonged high fat diets (HFD) induce low-grade chronic intestinal inflammation in mice, and diets high in saturated fat are a risk factor for the development of human inflammatory bowel diseases. We hypothesized that HFD-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/oxidative stress occur in intestinal secretory goblet cells, triggering inflammatory signaling and reducing synthesis/secretion of proteins that form the protective mucus barrier. In cultured intestinal cells non-esterified long-chain saturated fatty acids directly increased oxidative/ER stress leading to protein misfolding. A prolonged HFD elevated the intestinal inflammatory cytokine signature, alongside compromised mucosal barrier integrity with a decrease in goblet cell differentiation and Muc2, a loss in the tight junction protein, claudin-1 and increased serum endotoxin levels. In Winnie mice, that develop spontaneous colitis, HFD-feeding increased ER stress, further compromised the mucosal barrier and increased the severity of colitis. In obese mice IL-22 reduced ER/oxidative stress and improved the integrity of the mucosal barrier, and reversed microbial changes associated with obesity with an increase in Akkermansia muciniphila. Consistent with epidemiological studies, our experiments suggest that HFDs are likely to impair intestinal barrier function, particularly in early life, which partially involves direct effects of free-fatty acids on intestinal cells, and this can be reversed by IL-22 therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-fat diet promotes experimental colitis by inducing oxidative stress in the colon.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):G453-G462. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00103.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31411504
-
IL-10 promotes production of intestinal mucus by suppressing protein misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress in goblet cells.Gastroenterology. 2013 Feb;144(2):357-368.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.043. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23123183
-
Meat proteins in a high-fat diet have a substantial impact on intestinal barriers through mucus layer and tight junction protein suppression in C57BL/6J mice.Food Funct. 2019 Oct 16;10(10):6903-6914. doi: 10.1039/c9fo01760g. Food Funct. 2019. PMID: 31588474
-
Mucosal barrier, bacteria and inflammatory bowel disease: possibilities for therapy.Dig Dis. 2014;32(4):475-83. doi: 10.1159/000358156. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Dig Dis. 2014. PMID: 24969297 Review.
-
High-fat diet induces intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in ulcerative colitis: emerging mechanisms and dietary intervention perspective.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):653-677. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36915785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prebiotic oligofructose protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity by changing the gut microbiota, intestinal mucus production, glycosylation and secretion.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2152307. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2152307. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 36448728 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved multi-omics reveals diverse metabolic strategies of Salmonella during diet-induced inflammation.mSphere. 2024 Oct 29;9(10):e0053424. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00534-24. Epub 2024 Sep 10. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39254340 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal plasticity and metabolism as regulators of organismal energy homeostasis.Nat Metab. 2022 Nov;4(11):1444-1458. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00679-6. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Nat Metab. 2022. PMID: 36396854 Review.
-
Elateriospermum tapos Yogurt Supplement in Maternal Obese Dams during Pregnancy Modulates the Body Composition of F1 Generation.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 2;15(5):1258. doi: 10.3390/nu15051258. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904258 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids Prevent Altered-Muc2 Secretion Induced by Palmitic Acid by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in LS174T Goblet Cells.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 11;11(9):2179. doi: 10.3390/nu11092179. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31514316 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

