Atypical calcium regulation of the PKD2-L1 polycystin ion channel
- PMID: 27348301
- PMCID: PMC4922860
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13413
Atypical calcium regulation of the PKD2-L1 polycystin ion channel
Abstract
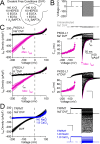
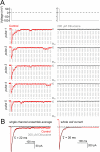
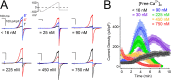
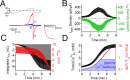
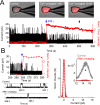
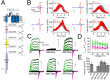
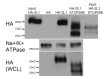
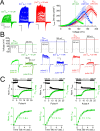
Native PKD2-L1 channel subunits are present in primary cilia and other restricted cellular spaces. Here we investigate the mechanism for the channel's unusual regulation by external calcium, and rationalize this behavior to its specialized function. We report that the human PKD2-L1 selectivity filter is partially selective to calcium ions (Ca(2+)) moving into the cell, but blocked by high internal Ca(2+)concentrations, a unique feature of this transient receptor potential (TRP) channel family member. Surprisingly, we find that the C-terminal EF-hands and coiled-coil domains do not contribute to PKD2-L1 Ca(2+)-induced potentiation and inactivation. We propose a model in which prolonged channel activity results in calcium accumulation, triggering outward-moving Ca(2+) ions to block PKD2-L1 in a high-affinity interaction with the innermost acidic residue (D523) of the selectivity filter and subsequent long-term channel inactivation. This response rectifies Ca(2+) flow, enabling Ca(2+) to enter but not leave small compartments such as the cilium.
Keywords: TRP channels; biophysics; calcium signaling; cell biology; channel desensitization; human; ion channel biophysics; ion selectivity; polycystic kidney disease; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
DEC: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
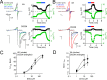

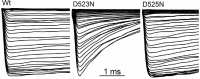
Comment in
-
Polycystic kidney disease: Exiting Ca(2+) inactivates polycystin-2L1.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Sep;12(9):508. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.112. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27425162 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structure of the polycystin 2-l1 ion channel.Elife. 2018 Jul 13;7:e36931. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36931. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30004384 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution structure of the EF-hand domain of human polycystin-2.Protein Sci. 2014 Sep;23(9):1301-8. doi: 10.1002/pro.2513. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24990821 Free PMC article.
-
Influx-Operated Ca(2+) Entry via PKD2-L1 and PKD1-L3 Channels Facilitates Sensory Responses to Polymodal Transient Stimuli.Cell Rep. 2015 Oct 27;13(4):798-811. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.041. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26489466
-
Determining the Crystal Structure of TRPV6.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 14. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 14. PMID: 30299652 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
TRP channels and kidney disease: lessons from polycystic kidney disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Feb;35(Pt 1):124-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0350124. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17233617 Review.
Cited by
-
Energetic landscape of polycystin channel gating.EMBO Rep. 2023 Jul 5;24(7):e56783. doi: 10.15252/embr.202356783. Epub 2023 May 9. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37158562 Free PMC article.
-
Primary cilium: a paradigm for integrating mathematical modeling with experiments and numerical simulations in mechanobiology.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Jan 15;18(2):1215-1237. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021066. Math Biosci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33757184 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanotransduction Mechanisms in Mitral Valve Physiology and Disease Pathogenesis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Dec 22;4:83. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00083. eCollection 2017. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 29312958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of polycystin channels in primary cilia.Cell Signal. 2020 Aug;72:109626. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109626. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32251715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The asparagine 533 residue in the outer pore loop region of the mouse PKD2L1 channel is essential for its voltage-dependent inactivation.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Aug 14;7(9):1392-1401. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12273. eCollection 2017 Sep. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28904867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben-Johny M, Dick IE, Sang L, Limpitikul WB, Kang PW, Niu J, Banerjee R, Yang W, Babich JS, Issa JB, Lee SR, Namkung H, Li J, Zhang M, Yang PS, Bazzazi H, Adams PJ, Joshi-Mukherjee R, Yue DN, Yue DT. Towards a Unified Theory of Calmodulin Regulation (Calmodulation) of Voltage-Gated Calcium and Sodium Channels. Current Molecular Pharmacology. 2015;8:188–205. doi: 10.2174/1874467208666150507110359. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boulter C, Mulroy S, Webb S, Fleming S, Brindle K, Sandford R. Cardiovascular, skeletal, and renal defects in mice with a targeted disruption of the Pkd1 gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98:12174–12179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.211191098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

