Staphylococcus aureus SaeR/S-regulated factors reduce human neutrophil reactive oxygen species production
- PMID: 27334228
- PMCID: PMC5069094
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.4VMAB0316-100RR
Staphylococcus aureus SaeR/S-regulated factors reduce human neutrophil reactive oxygen species production
Abstract
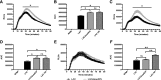
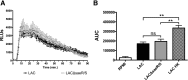
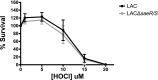
Neutrophils are the first line of defense after a pathogen has breached the epithelial barriers, and unimpaired neutrophil functions are essential to clear infections. Staphylococcus aureus is a prevalent human pathogen that is able to withstand neutrophil killing, yet the mechanisms used by S. aureus to inhibit neutrophil clearance remain incompletely defined. The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a vital neutrophil antimicrobial mechanism. Herein, we test the hypothesis that S. aureus uses the SaeR/S two-component gene regulatory system to produce virulence factors that reduce neutrophil ROS production. With the use of ROS probes, the temporal and overall production of neutrophil ROS was assessed during exposure to the clinically relevant S. aureus USA300 (strain LAC) and its isogenic mutant LACΔsaeR/S Our results demonstrated that SaeR/S-regulated factors do not inhibit neutrophil superoxide (O2-) production. However, subsequent neutrophil ROS production was significantly reduced during exposure to LAC compared with LACΔsaeR/S In addition, neutrophil H2O2 production was reduced significantly by SaeR/S-regulated factors by a mechanism independent of catalase. Consequently, the reduction in neutrophil H2O2 resulted in decreased production of the highly antimicrobial agent hypochlorous acid/hypochlorite anion (HOCl/-OCl). These findings suggest a new evasion strategy used by S. aureus to diminish a vital neutrophil antimicrobial mechanism.
Keywords: bacteria; host-pathogen interactions; innate immunity; two-component systems.
© Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures
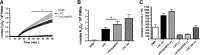
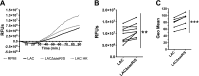
Similar articles
-
Nutritional Regulation of the Sae Two-Component System by CodY in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00012-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-18. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378891 Free PMC article.
-
Epic Immune Battles of History: Neutrophils vs. Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;7:286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00286. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28713774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SaeR/S gene regulatory system is essential for innate immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus.J Infect Dis. 2009 Jun 1;199(11):1698-706. doi: 10.1086/598967. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19374556 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cis-urocanic acid on bovine neutrophil generation of reactive oxygen species.J Dairy Sci. 2006 Nov;89(11):4188-201. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72464-X. J Dairy Sci. 2006. PMID: 17033005
-
Staphylococcus aureus versus neutrophil: Scrutiny of ancient combat.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jun;131:259-269. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.026. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31002964 Review.
Cited by
-
Network analysis for identifying potential anti-virulence targets from whole transcriptome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus exposed to certain anti-pathogenic polyherbal formulations.Drug Target Insights. 2023 May 29;17:58-69. doi: 10.33393/dti.2023.2595. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Drug Target Insights. 2023. PMID: 37275512 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-Sensing Under Hypochlorite Stress and Infection Conditions by the Rrf2-Family Repressor HypR in Staphylococcus aureus.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Sep 1;29(7):615-636. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7354. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 29237286 Free PMC article.
-
Immune evasion by a staphylococcal inhibitor of myeloperoxidase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 29;114(35):9439-9444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707032114. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28808028 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neutrophil myeloperoxidase inhibitor SPIN by the small RNA Teg49 in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jun;117(6):1447-1463. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14919. Epub 2022 May 31. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35578788 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus SaeRS impairs macrophage immune functions through bacterial clumps formation in the early stage of infection.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Oct 6;10(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00576-8. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39370453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amulic B., Cazalet C., Hayes G. L., Metzler K. D., Zychlinsky A. (2012) Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 30, 459–489. - PubMed
-
- Nordenfelt P., Tapper H. (2011) Phagosome dynamics during phagocytosis by neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 90, 271–284. - PubMed
-
- DeLeo F. R., Quinn M. T. (1996) Assembly of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase: molecular interaction of oxidase proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 60, 677–691. - PubMed
-
- DeLeo F. R., Allen L. A., Apicella M., Nauseef W. M. (1999) NADPH oxidase activation and assembly during phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 163, 6732–6740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

